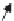Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
V
DD
RS
T
Pixel
TX
Drive
transistor
Pinned
PD
FD
RS
Load
transistor
φ
1
Column amplifier
with noise cancel
C
1
φ
2
C
2
G
=
C
1
/
C
2
φ
SH
C
SH
CS
Horizontal signal line
FIGURE 5.50
Column amplification with noise canceling function. (Reprinted with permission from Kawahito, S., Sakakibara,
M., Handoko, D., Nakamura, N., Satoh, H., Higashi, M., Mabuchi, K., and Sumi, H.,
Proceedings of the IEEE
International Solid-State Circuits Conference, Digest of Technical Papers
, 12.7, pp. 224-225, 2003.)
circuits to 1/
G
. As the column amplifiers work in parallel in bandwidths <1 MHz, noises
in higher frequency ranges generated in anterior stages, such as thermal noise in the tran-
sistors in the SFA, are also reduced. Amplified difference signal is sampled and held in
sampling capacitance
C
SH
at each column and output to the horizontal signal line by way
of the column select transistor CS.
5.3.3.1.2 High-Gain Double-Stage Noise Canceller
By amplifying the noise canceller described above, not only noise of both pixel and column
amplifiers, but also noise caused by the noise canceller are removed. The impact of noise
in the noise canceller is also suppressed. If column amplifier gain is high enough, the only
remaining noise is that originating from variation of charge quantity at the input node of
the column amplifier caused by kTC noise, which occurs when ϕ
2
is changed to off-state.
In a proposed configuration,39
39
the amplifying noise canceller in Figure 5.50 is followed by
the differential circuit discussed in Figure 6.42a as the second-stage differential circuit, as
shown in Figure 5.51.