Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
connected FDs increases. This means a decrease in the charge-voltage conversion factor,
that is, decrease of output voltage and charge quantity gain. Therefore, a balanced design
is required for overall performance.
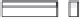
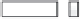
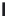
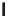
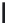
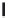
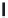
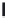
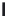
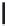
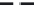
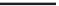
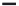
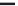
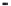
A means to reduce transistor number further is FD-drive architecture,
35,36
illustrated in
Figure 5.49. Figure 5.49a and b show examples of vertical four-shared pixel configuration
and horizontal and vertical four-shared pixel configuration, respectively. In Figure 5.49a,
the row select transistor (RS) is removed in comparison with Figure 5.48b.
In this type, FD potentials are kept lower than those in a situation filled with charges
are. At the row select operation, only the FDs of pixels belonging to the selected row are
set to the high voltage condition of clock voltage source
V
dd
by way of RST. Then, signal
charges are transferred from PD to FD as well as a normal 4-Tr pixel sensor. By this set-
ting, gate electrodes connected to FDs of driver transistors are set to lower voltage than
that of the selected pixel. Let us consider a situation where a number of drive transistors
are commonly connected to a vertical signal line in (5) in Figure 5.47, and among them only
one drive transistor has a gate electrode with higher voltage than the others. It is clear that
electrons flowing from
V
ss
to
V
dd
take the channel of lowest potential energy determined
by the selected pixel. This means that drive transistors of unselected rows are the same
in the off-situation, that is, it is equal to a situation where they are not selected, namely,
winner takes all.
In this configuration, six transistors are used for four pixels, so the number of transis-
tors per pixel is 1.5 Tr/pixel. In the case of a horizontal and vertical shared pixel, since FDs
are also shared by two horizontal pixels, as shown in the Figure 5.49b, this type has the
advantage of lower FD capacitance, that is, suppression of charge-voltage conversion fac-
tor decrease.
Since vertical shared pixel configuration has translation symmetry in both horizontal
and vertical directions, misalignment at patterning process gives the same effect to all
pixels. Performance uniformity between pixels is kept. On the other hand, horizontal and
vertical shared pixel configuration has translation symmetry only in the vertical direction.
V
dd
(clock voltage source)
V
dd
(clock voltage source)
Drive
transistor
Drive
transistor
RST
RST
TX1
TX1
TX3
p
+
p
+
n
-
FD
n
-
PD1
FD
PD1
PD3
TX2
TX2 TX4
FD
PD2
PD2
PD4
FD
TX3
FD
PD3
TX4
FD
(a)
PD4
(b)
FIGURE 5.49
FD-drive shared pixel configuration: (a) vertical four-shared pixel configuration (1.5 Tr/pixel); (b) horizontal
and vertical four-shared pixel configuration (1.5 Tr/pixel).