Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
10
0
10
-1
10
-2
10
-3
10
-4
10
-5
10
-6
0
0.04 0.08
Primary apparent bedload velocity,
n
b
(m/s)
0.12
0.16
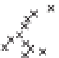
Fig. 2.6
Site-specifi c measured bed-load transport rate versus measured bed-load velocity. Symbols:
Agassiz (gravel bed) long
averages;
Agassiz (gravel bed) 5-minute samples;
×
Canoe Pass 2000 (sand bed); * Canoe Pass 2001 (sand bed);
Sea Reach
(sand bed).
From Rennie & Villard (2004).
from the log-law Keulegan equation (see below).
Bed-load transport rate was non-dimensionalized
using Einstein's formula (Einstein 1950):
above that value resulted from localized values of
g
b
being measured over large dunes. No correlation
existed between
v
b
and
g
b
measured from physical
sampling. It was suggested that physical sampling
was an unsatisfactory method for characterizing
g
b
at the higher transport rates found in the lower
Missouri River, USA.
Gaeuman & Jacobson (2006) also modeled the
relation between the average particle velocity,
v
p
, and
the apparent bed velocity measured by the ADCP.
The average particle velocity was calculated using the
van Rijn (1984) formula, a shear stress approach.
The spatially averaged surface particle velocity (
v
pa
)
can be assumed to vary from a value much lower
than the calculated
v
p
near entrainment (because
much of the bed surface is immobile) to a value
approaching the calculated
v
p
at higher transporting
conditions (Gaeuman & Jacobson 2006).
g
b
g
*
=
(4)
b
3
ρ
(
S
−
1
)
gd
s
s
50
where:
S
s
is the sediment specifi c gravity;
g
is the
gravitational acceleration; and
d
50
is the bed-load
median grain size. It was found that 42% of the
variance in
g
*
was explained by variance in
v
b
/
u
*.
Apparent bed velocity was correlated to bed-load
transport rate from physical sampling and dune
tracking in the lower Missouri River (Gaeuman &
Jacobson 2007). Measurements were taken in the
thalweg, which consisted of a sand bed with dunes.
Physical bed-load sampling used a Helley-Smith
sampler in 2004 and a US BL-84 sampler (Kuhnle
2008) in 2005. Apparent bed velocity was correlated
with
g
b
measured from dune tracking for values
lower than 0.9 kg/(m-s), whereas large variability
vvww
b
=
(5)
p
b
f