Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
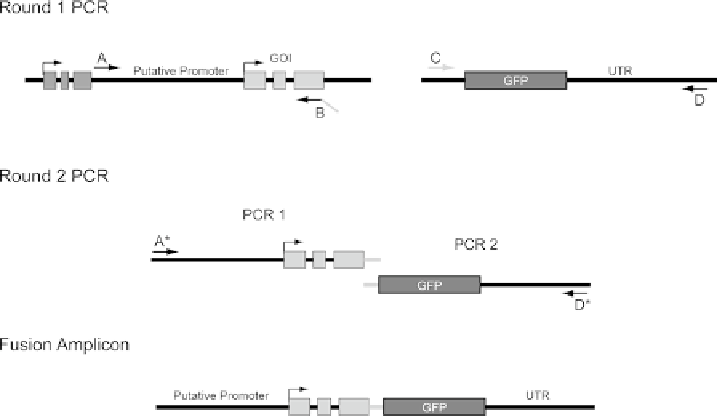
Fig. 10
PCR stitching. The approach requires two rounds of PCR amplification. In the first round, the
genomic region of interest (a promoter element or full-length gene) is amplified while in a separate
reaction the reporter element is also amplified. Primer B is designed with a 20 bp ''tail'' with homology to
the 5
'
end of the reporter element. In the second round, DNA from the two PCRs are combined into a single
reaction. Subsequent amplification is performed with nested external primers. The presence of the 20 bp
region of homology acts as an internal priming site for the two DNA fragments facilitating the amplifi-
cation of a fusion product.
of material that may require additional cloning steps if the construct is required in
large amounts.
4. Recombineering
Since regulatory elements that affect gene expression can reside within introns or
downstream of a gene (
Conradt and Horvitz, 1999
) and many genes are regulated at
the post-transcriptional level (
Ambros, 2004
), it is essential to include these elements
in an expression construct if an accurate representation of the expression pattern is to
be achieved. Recombination-mediated methods to engineer fluorescent protein
fusions in the context of genomic clones are therefore an attractive approach to use
(
Bamps and Hope, 2008; Dolphin and Hope, 2006; Sarov et al., 2006; Tursun et al.,
2009
). The availability of a C. elegans fosmid library (
http://elegans.bcgsc.bc.ca/
) that
covers
80% of the genome (D. Moerman, personal communication) is an essential
resource that has made this approach feasible. The relatively large genomic fragments
containing fosmids (
35 kb) combined with the redundant coverage of the fosmid
library means that a suitable genomic clone containing the gene of interest and
surrounding cis-regulatory control elements can be identified in most cases.
Recombineering relies on homologous recombination between a reporter con-
struct and genomic clone mediated by bacteria expressing the
l
Red recombinase
Search WWH ::

Custom Search