Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
development. These include the activation and/or degradation of selected maternal
mRNAs and proteins, release of cortical granules (CGs), secretion of a chitinous
eggshell, and the mounting a membrane block to polyspermy to prevent fertilization
by a second sperm (
Horner andWolfner, 2008; Marcello and Singson, 2010; Singson
et al., 2008; Stitzel et al., 2007
). If all of these processes are coordinated and
completed properly, the embryo will develop as it passes through the uterus and is
eventually laid at approximately the 30-cell stage (
Ringstad and Horvitz, 2008;
Singson et al., 2008
).
In mutagenesis or RNAi screens, egg-sterile animals (egg) with defects in either
sperm-egg fusion or egg activation are identified in the same way as spe mutants.
Animals are screened for mutants that lay ''eggs'' that either possess weak, osmot-
ically sensitive eggshells (
Fig. 2E
) or lack eggshells altogether (
Fig. 2D
). To distin-
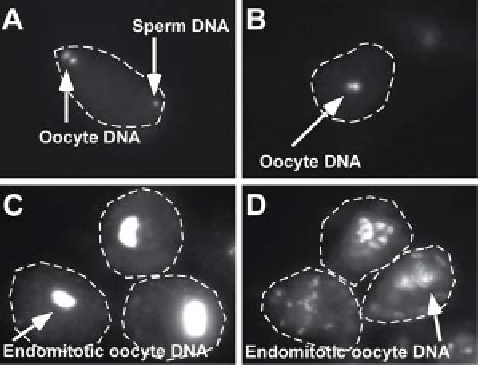
guish egg-activation defect mutants from fertilization defective mutants, DAPI
staining can be used to score young meiotic stage ''eggs'' within the spermatheca
or uterus for the presence of sperm chromatin (sperm entry) (
Fig. 7
).
If mutant oocytes remain unfertilized, they will lack both a sperm chromatin mass
and meiotic polar bodies (
McNally and McNally, 2005
)(
Fig. 7B
). In unfertilized
oocytes, the maternal chromosomes initiate the meiotic divisions and reach ana-
phase I but the resulting anaphase chromosome masses subsequently decondense to
form two distinct pronuclei. These unfertilized oocytes fail to form polar bodies or
attempt the second meiotic division (
McNally and McNally, 2005
). During the
subsequent rounds of endomitotic cell cycling they form a single, large, polyploid
DNA mass (
Chatterjee et al., 2005; Doniach and Hodgkin, 1984; Miller et al., 2003
)
(
Fig. 7C
).
Fig. 7
DAPI-stained dissected oocytes. (A) Newly fertilized oocyte with both oocyte DNA and a
visible sperm chromatin mass. (B) Unfertilized oocytes lacking a sperm chromatin mass. (C) Older
endomitotic unfertilized oocyte. (D) Older endomitotic egg-activation mutant oocyte.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search