Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
immunoprecipitations or TAPs for mass spectrometry. The required buffers, solu-
tions, and equipment are listed in Sections X and XI.
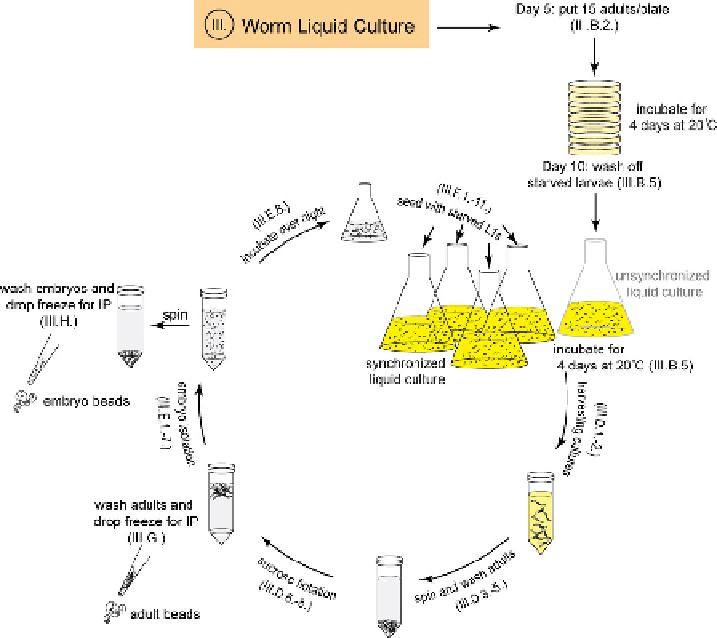
The standard procedure for liquid cultures is outlined in
Fig. 4
. First, adult worms
are grown on OP-50 seeded 100 mm NGM agarose plates to obtain starved larvae
that are used to initiate an unsynchronized liquid starter culture. Adults are har-
vested, embryos isolated by bleaching and hatched as L1s in the absence of food.
Synchronized L1s are used to set up the second round of liquid culture and worms or
embryos are harvested for extract generation. Worms and embryos can be stored at
Fig. 4
Schematic overview of worm liquid culture (see Section III.). Fifteen axenized adults are grown
4 days on 100 mm NGM agarose plates until larvae are starved (Section III.B.2.). Starved larvae are
washed off the NGM plates and used to inoculate an unsynchronized liquid culture (Section III.B.5.).
After 4 days, adult worms with 10-15 embryos are harvested, washed with M9, and cleaned by sucrose
flotation (Section III.D.1.-8.). Embryos are isolated by bleaching and incubated overnight for L1 larvae
to hatch (Section III.E.1.-8.). Starved L1 larvae are used to inoculate synchronized liquid culture
(Section III.F.1.-11.). Harvested worms (Section III.G.) and embryos (Section III.H.) are drop frozen
in liquid nitrogen for subsequent extract preparation. Roman numeral indicates corresponding section.
(See color plate.)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search