Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
3.2
Expression of HS Biosynthetic Enzymes in
E. coli
HS biosynthetic enzymes are traditionally expressed in mammalian or insect cells
[36-39]. We have expressed these enzymes in bacteria that coexpresses a chaper-
one protein, which dramatically reduces the difficulty in obtaining the enzymes in
large quantities [40-53]. We used a bacterial cell line that coexpresses chaperone
GroEL/GroES to achieve high levels of expression by taking advantage of the fact
that the chaperone helps the proteins fold correctly. These recombinant proteins
have specific activities and substrate specificity comparable of those expressed in
insect cells (Table 1).
3.3 Coupling HS Sulfotransferase with a PAPS
Regeneration System
PAPS is the sulfo donor for sulfotransferases. The PAPS regeneration system, ini-
tially developed by Wong's lab [54], has been applied in HS/heparin enzymatic
synthesis [40]. PAP is formed when the sulfo group is transferred to an acceptor.
However, PAP inhibits the HS sulfotransferases activity, making milligram-scale
synthesis difficult without continuously removing PAP. The PAPS regeneration
(p-nitrophenol sulfate (PNPS))
(p-nitrophenol (PNP))
O
2
N
OSO
3
H
O
2
N
OH
Arylsulfotransferase IV(AST-IV)
PAP
PAPS
SO
3
-
OH
OH
O
2, 6, 3-OST
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
HO
HO
HO
O
HOOC
OH
O
HO
HOOC
NHSO
3
-
OH
NHSO
3
-
Fig. 4
PAPS regeneration system. A PAPS regeneration system converts PAP to PAPS through
the action of recombinant arysulfotransferase-IV, which catalyzed the transfer of sulfo group from
p-nitrophenyl sulfate (PNPS) to PAP. Thus, HS sulfotransferases use PNPS, instead of PAPS, as
the sulfo donor



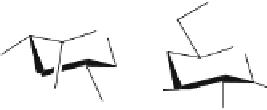









Search WWH ::

Custom Search