Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
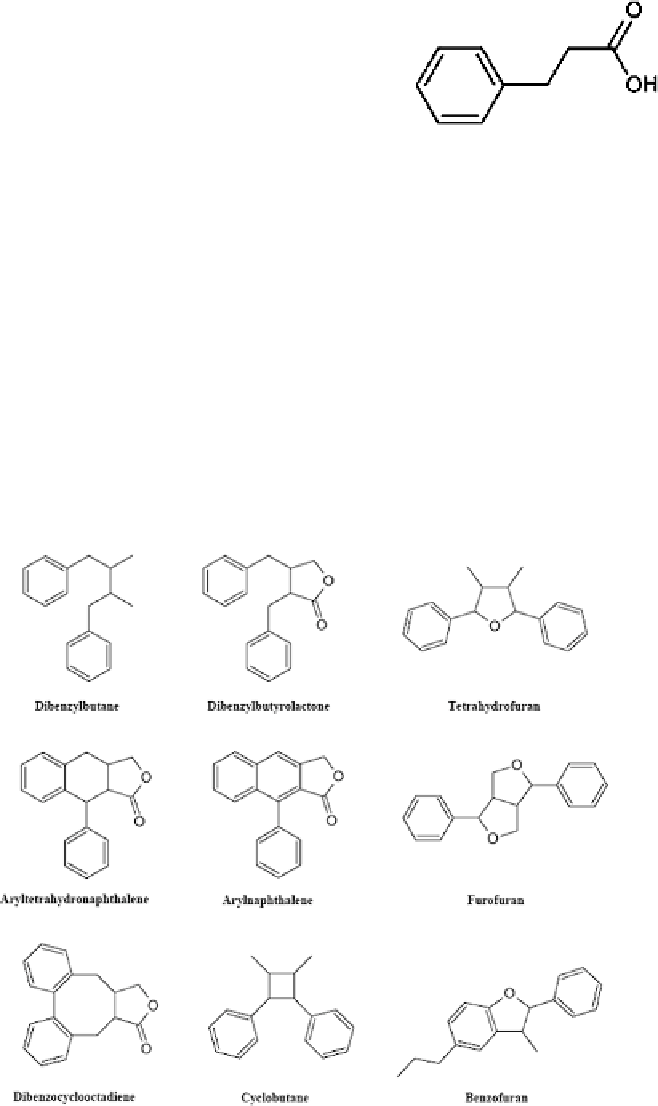
Fig. 1
Cinnamic acid residue
of plants, roots, leaves, flowers, fruits and seeds [6]. Dimerization of the cinnamic
acid residues, oxygen incorporation, and skeletal functionalization may occur in
different ways giving a great diversity of structures. The important lignan skeletons
are being listed in Fig. 2. The biological role of lignans in plants is related to the
plant defence as well as to the regulation of its growth [7]. Due to a wide range
of biological activities, including antifungal, antitumor, antiviral, hepatoprotective,
and other properties, lignans are of considerable nutritional and pharmacological
interest [8-10]. In vitro, animal, and epidemiological studies also suggest that these
compounds may have cancer preventive properties through a variety of mechanisms,
including anti-estrogenic, antiangiogenic, antioxidant, and pro-apoptotic properties
[11, 12]. Lignans are one of three main groups of plant compounds classified as phy-
toestrogens, the other two being isoflavonoids and coumestans. All three groups are
structurally similar to estrogens, which are known to modulate immune functions in
humans [13, 14].
Fig. 2
Representative skeletons of lignans
Search WWH ::

Custom Search