Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
a
b
Organic matter
NADH
+
H
+
Hydrolysis
NADH
+
H
+
Simple Molecules
NADH-dehydrogenase
NADH
+
H
+
NAD
+
+
2H
+
Phospho-enol-pyruvate
Fd
ox
Hydrogenase
2e
-
Fd
red
NADH
+
H
+
Pyruvate
H
2
NADH
+
H
+
PDC
Ethanol
+/ H
2
Butyrate
+
2H
2
Propionate
-
Malate
H
2
Acetate
+
4H
2
-
2H
2
-
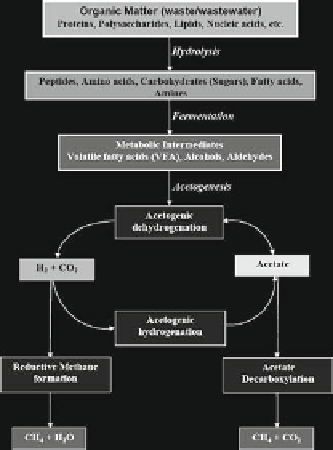
Fig. 1
(
a
) Anaerobic process depicting both acidogenic and methanogenic processes during con-
version of complex organic molecules through biohydrogen to methane and carbon dioxide; (
b
)
Metabolic pathways relating to possible routes of H
2
formation from proton (H
+
) generated during
substrate degradation
which also include acetate production from H
2
and CO
2
by acetogens and homoace-
togens and finally acetoclastic methanogens convert organic acids to CH
4
and CO
2
[4, 11, 13]. H
2
-producing AB grow in syntrophic association with hydrogenotrophic
methanogens (H
2
consuming), resulting in low H
2
partial pressure thus allowing
acetogenesis to become thermodynamically favorable by interspecies H
2
transfer
[11].














Search WWH ::

Custom Search