Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
The velocity distribution in a trapezoidal, earthen irrigation canal has
been measured (Paudel, 2010) and for the rough canal the coefficient
β
has been determined:
sin
θ
exp
0
.
8
y
h
1
β
=
−
(5.90)
where:
h
1
=
water depth at point 1 (m)
θ
=
angle made by side slope with the water surface
β
=
correction factor for the dip phenomenon
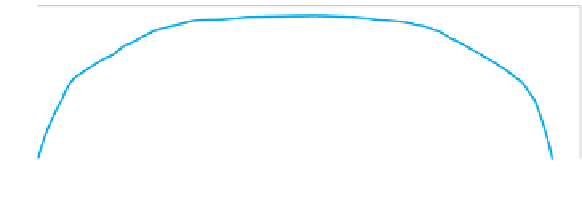
Figure 5.22 shows the velocity distribution as predicted by the equation
and measured in the irrigation canal.
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
2.0
Distance (m)
3.0
4.0
1.0
Calculated
Measured
3.82 m
0.72 m
Figure 5.22. Examples of
calculated and measured
velocity distribution in an
earthen irrigation canal.
2.40 m
5.3.6
Exponent of the velocity in the sediment transport predictors
Sediment transport predictors are in different forms and complexities
depending upon the assumptions and the basic approaches used in the
derivation of the predictor. There is no general agreement on the type of
variables that are required to define the sediment transport, but the most
frequently used ones are:
q
s
=
f
(
u
,
h
,
S
,
ρ
,
ν
,
ρ
s
,
d
50
,
g
,
σ
g
)
(5.91)








































Search WWH ::

Custom Search