Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Acid-base accounting involves measurement of the maximum potential acidity (MPA) and the
acid neutralizing capacity (ANC), with the net acid producing potential (NAPP) calculated as
the difference between the two values. The MPA is calculated from the total sulphur content,
determined by the Leco furnace method, assuming that all the sulphur occurs as pyrite, which
oxidizes to generate acid according to the following reaction:
→
FeS
2
15/4O
2
7/2H
2
O
Fe(OH)
3
2H
2
SO
4
(17.2)
The MPA of a sample is calculated from the sulphur content according to the following
formula:
MPA(kg H
2
SO
4
/t)
(Total %S)
30.6
(17.3)
The presence of sulphate minerals such as anhydrite and/or the presence of sulphide min-
erals with a lower sulphur content would result in the MPA being signii cantly overstated.
The ANC represents the inherent acid buffering of the sample. It is determined by the
Modii ed Sobek method in which the sample is reacted with hydrochloric acid (HCl), fol-
lowed by back-titrating with sodium hydroxide (NaCl) to quantify the unreacted HCl.
The acid consumed by the reaction (HCl added minus unreacted HCl) is then expressed
as kg H
2
SO
4
/t of sample.
The NAPP, which may be positive or negative, is the difference between MPA and ANC:
i.e. NAPP
MPA
ANC
(17.4)
The ANP/MPA ratio provides an indication of the risk of acid generation from mine
wastes. A positive NAPP equates to an ANC/MPA of less than 1, while a negative NAPP
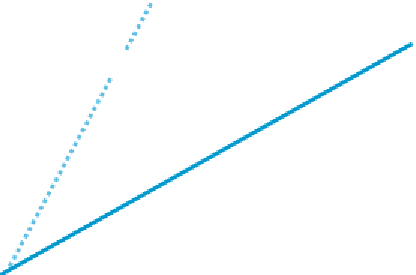
represents an ANC/MPA of more than 1. Acid-base account results are commonly pre-
sented on a plot as shown on
Figure 17.5
.
The NAG test involves reaction of a sample with hydrogen peroxide (H
2
O
2
) which oxi-
dizes the contained sulphide minerals. As both acid generation and neutralization reactions
occur simultaneously in this reaction, the resultant NAG capacity is a direct measure of the
amount (rather than the potential amount as in the NAPP test) of acid generated, as evaluated
from the pH and acidity of the NAG liquor, after cooling. The forms of acidity may be deter-
mined by titration to pH 4.5 which determines acidity due to free acid, then continuing the
titration to pH 7 which determines acidity due to soluble iron and alumina. The Sequential
The ANP/MPA ratio provides
an indication of the risk of acid
generation from mine wastes.
150
NAPP = 0
ANC/MPA = 2
ANC/MPA = 3
FIGURE 17.5
Acid-base Account Plot
ve NAPP
100
Source:
Miller & Jeffery 1995
ve NAPP
50
0
1
2
3
4
5
Total S (%)
ANC - Acid Neutralization Capacity
MPA - Maximum Potential Acidity
NAPP - Net Acid Producing Potential
S - Sulphur












Search WWH ::

Custom Search