Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
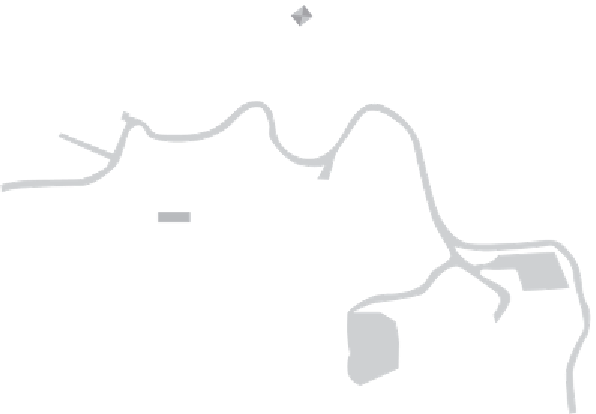
Cooling water is used in various mine processes for the purpose of removing heat from
equipment, process operations and materials. Typically, spent cooling water is combined
with other efl uent streams such as a tailings slurry discharge to a tailings pond (e.g. pro-
cess efl uent) or mine water stream, prior to discharge to the environment.
Mine water results from the dewatering of underground or open pit mining operations.
It is typically pumped from the mine and either added to the process water supply or dis-
charged through settling ponds or combined with process efl uent.
Seepage comprises water discharged to the environment by seepage from waste man-
agement areas (e.g. tailings ponds or waste rock dumps) or wastewater impoundment
areas (e.g. clarii cation or mine water ponds).
Storm water from a mining operation comprises surface runoff from rainfall, snow-
melt, and natural drainage. Storm water discharges associated with mining operations can
include but are not limited to drainage from mine and mill sites; drainage collection ponds;
material handling areas; raw material storage sites; and waste disposal areas, including
waste rock and overburden dumps. Typically, drainage is diffuse, with a large number of
discharge points to the environment. In many projects, storm water is collected and stored
for use in mine processes. In other cases it is discharged to the environment after i rst pass-
ing through one or more settling ponds.
Other efl uent streams on a mine site include sanitary wastewater discharges, emer-
gency overl ows from wastewater impoundment ponds, and backwash waters from pota-
ble water treatment plants.
Acid rock drainage also counts as mine efl uent, and will be discussed in more detail in
the following section.
Typically, drainage is diffuse, with
a large number of discharge
points to the environment.
Seepage
Creek
Effluent Treatment
Plant
Final Discharge Point
Polishing
Pond
Mine Water
Settling
Pond
Storm Water
Tailings
Basin
Mine Water Ponds
Tailings
Pipeline
Process
Water
Mine & Mill
Storm Water
Low Grade Ore
Stock Pile
Overburden
Dump
FIGURE 13.6
Typical Mine Site and Effl uent Streams
Open
Pit
Storm Water
Waste Rock
Stockpile
River
In mining, water is both friend and foe.
Water is consumed in large quantities
as process water to extract minerals.
It can also be the most devastating dis-
ruptive force both from the standpoint
of its physical impact as well as
a carrier of unwanted contaminants.
Source:
Adopted from
www.ec.gc.ca
Water Treatment
Plant
Storm Water
Lake
Creek


























































Search WWH ::

Custom Search