Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
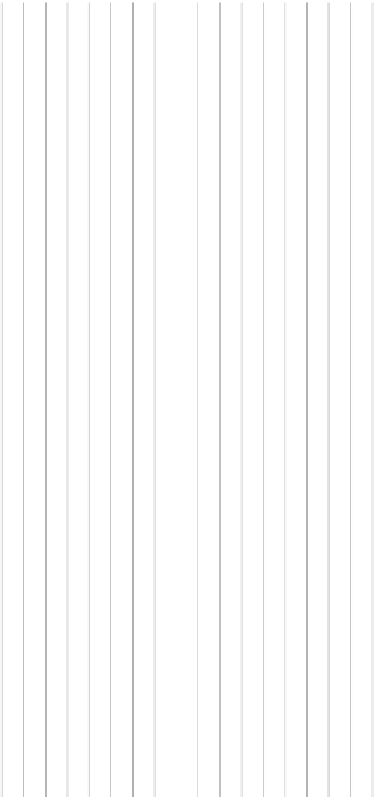
Simple Checklist Matrix
- The simple checklist matrix (Leopold 1971) can be used to
identify impacts by systematically checking each project activity against each environmen-
tal component. If a particular activity is considered to have the potential to affect a par-
ticular environmental component, a mark is placed in the cell at the intersection of activity
and environmental component, highlighting the need for further studies (
Figure 9.7
).
Descriptive information on the nature and magnitude of impacts may replace the mark,
providing information rather than just identifying whether the impact would occur or
not. Patterns in completed matrices, for example columns or rows with numerous impact
strikes, help to illustrate cumulative impacts on a particular environmental receptor.
Likely impact interactions can also be identii ed.
Weighted matrices
- Some matrix applications allow the matrix to be weighted to rel ect
factors such as duration, frequency and extent of impacts, or to score or rank impacts.
Patterns in completed matrices,
for example columns or rows
with numerous impact strikes,
help to illustrate cumulative
impacts on a particular
environmental receptor.
Environmental
effects
Social environment
Physical environment
Biological environment
Development
Prospecting Surveys
Drilling
Sampling
Overburden stripping
Blasting
Dewatering
Crushing
Methods used
Ventilating system
Dewatering
Floating plant
Pond formation
Water supply
Washing plant
Process used
Stockpiling
Wastewater treatment
Wastewater disposal
Opencast
mining
Under-
ground
mining
Dredging
Ore
Processing
Tailings
Tailings dam
Runoff control
Contour shaping
Planting
Overburden use
Rehabilita-
tion
General
Surface infrastructure
Access road
Energy source
FIGURE 9.7
Leopold Matrix
This simple checklist matrix can be used to identify impacts by systematically checking each project activity against each environmental component.




















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search