Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
To this end, the designing of an online learning
environment according to constructivist school
focuses on the active participation of students in
learning process i.e. the system should keep learn-
ers active doing high-level activities. Prerequisite
for the fulfillment of this objective is the interac-
tion of learners with the educational material in
order to discover or create new knowledge. Web-
based simulations constitute a typical case of such
interactive learning applications, in which each
action of learner within virtual environment is
interpreted in new knowledge. On the other hand,
the communication among members of a learning
process is of great importance in constructivism,
since it allows the exchange of experiences and
ideas resulting in a better interpretation of the
available information. As stated e.g. in (Hooper
& Hannafin, 1991), collaborative and cooperative
learning should be encouraged to facilitate con-
structivist learning. Working with other learners
gives students real-life experience and allows
them to use and improve their meta-cognitive
skills. Finally, learners should have the control of
the educational procedure, as the main goal of
constructivism is to give stimulus to students to
discover or create the knowledge. However, the
application should support a form of guided dis-
covery, i.e. students can make their-own decisions
but they can also use some guidance from the
instructor.
One of the main benefits of constructivism
theory is that it considers learners as the centre
of learning process. Consequently, the construc-
tivist approach implies that learners will learn
more with a teacher than from a teacher (Newby,
1996) and that they will learn more with a virtual
learning environment than from a virtual learning
environment.
Collaborative Learning
Collaboration between learners and teachers is a
common request of various pedagogical methods
(e.g. constructivism). In online education, the
concept of collaborative learning is considered
essential for the performance of classroom-like
tasks and a prerequisite for the creation of a vir-
tual classroom. The term collaborative learning
refers to an instruction method, in which students
at various performance levels work together in
small groups towards a common educational
goal (Gokhale, 1995). In contrast with previous
pedagogical approaches, in which learners are
considered to be isolated, collaborative learning
introduces the concept of 'group'. In groups,
learners are able to cooperate, exchange ideas and
share experiences in order to acquire knowledge
on specific thematic areas.
Current Web technologies are considered suit-
able for the development of collaborative learning
environments due to their interactive functional-
ities. Collaboration can be achieved in two ways,
either synchronously or asynchronously. Synchro-
nous communication involves the participation of
both students and teacher at the same time e.g.
teleconference, while in asynchronous communi-
cation, which is more common, there is complete
time flexibility. That is, teachers and students do
not need to participate in learning process at the
same time (e-mail is the most common type of
asynchronous communication).
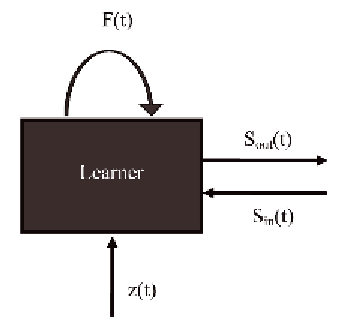
Figure 4. The learning model of constructivism
Search WWH ::

Custom Search