Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
of the system. The mostly applied pedagogical
methods used for this purpose are outlined below.
diagnostic tests, or on tests within the sequence
of learning activities and iv) demonstrate the
required operation, procedure or skill, and break
it down into its parts with appropriate explanation
before learners are expected to copy the desired
behavior. Learners are supposed to build profi-
ciency from frequent review or revision with
check tests at strategic points or repeat practice
with feedback (Modritscher, 2006). In general, a
designing approach with respect to behaviourism
theory considers a student as a passive recipient
and thus a well-structured learning material is
required to facilitate the acquisition of a new
behaviour through rehearsal and correction
(Tuckey, 1992).
Behaviorism
Behaviorism theory considers human mind as a
black box and regards that a response to a stimulus
can be quantitatively observed, ignoring totally the
impact of thinking occurring in mind (Modritscher,
2006). In essence, the behaviourism school focuses
on measurable and observable facts excluding
ideas, emotions and processes performed in
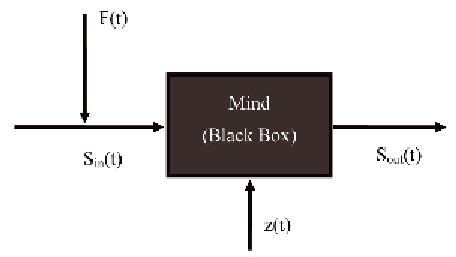
mind. In (Dietinger, 2003), Dietinger presents
a graphical representation (Figure 2) in order to
describe a learning model based on behaviorism
theory. According to this model S
in
(t) is the input
signal, F(t) is the external feedback, S
out
(t) is the
external signal, while the variable z(t) stands for
the observed events.
Atkins (Atkins, 1993) has studied the effect
of behaviourism theory on web-based distance
education defining basic rules regarding the
structure of educational content. Specifically,
course designer should: i) divide learning content
into small conceptual units and instructional steps,
ii) define sequences of instructions using either
conditional or unconditional branches to other
instructional units and pre-determining choices
within the course, iii) To maximize learning ef-
ficiency, learners may be routed to miss or repeat
certain sections based on the performance on
Cognitivism
In contrast with behaviorism, cognitivism theory
focuses on human's mind processes, such as
thinking, memory etc. The primary objective of
cognitivism is to discover, identify and model
the mental process performed into student's
mind during the learning process (Conlan, 2002).
Hence, in a cognitive approach, student's mind
is not considered as a passive black box (Figure
3 presents the learning model of cognitivism ac-
cording to Dietinger), but as a complex device,
which receives information from the environment,
processes this information and stores the outcome
to a short-term or a long-term memory. A perma-
Figure 2. The learning model of behaviorism according to Dietinger
Search WWH ::

Custom Search