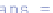Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 1.5 MATLAB
command history view
®
copy a former command in the history view and to paste it in the command window.
The user may wish to perform some alterations in the command and can do that
easily, before the command is executed after pressing the return button.
In the command window the up-arrow and down-arrow keys of the keyboards
offer an alternative, allowing a sequential loop through former commands.
1.2.2 Matrices in MATLAB
®
The name 'MATLAB' is a combination of 'matrix' and 'laboratory.' With respect
to the suite of various mathematical tools, which are made available by recent
versions of the software, one might think the origin of the MATLAB
®
software is
numerical linear algebra. A comprehensive treatment of matrix algebra is given by
Robbin (
1995
).
A
matrix
is a 2-dimensional array of numbers, for which examples are given
right below. Matrices can be specified directly by the user. Entries in lines are
separated by blanks; lines are separated by ';'.
The example matrix has two rows and three columns. Matrix dimensions are
2 and 3.
A
is a 2
3 matrix. It is thus non-square, as a
square matrix
has the same
number of rows and columns. Once a matrix is constructed, its elements can be
called by using usual round brackets, which is exemplified by:
The element in the second row and first column of A is 4. The first counting
index is 1, in contrast to conventions in other programming languages.