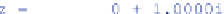Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 15.1 Analytical elements for some fundamental flow patterns
Element
(Real) Potential
'
Streamfunction
C
Baseflow
2
Q
x
0
x Q
y
0
y
Q
x
0
y þ Q
y
0
x
q
x x
well
Well
3
Q
2
Q
2
y
y
well
x x
well
2
2
log
ð
Þ
þ y y
well
ð
Þ
arctan
p
p
q
x x
0
Vortex
4
A
p
y
y
0
x x
0
A
p
2
2
arctan
log
ð
Þ
þ y y
0
ð
Þ
b
b
Di-pole
5
yy
0
xx
0
yy
0
xx
0
cos arctan
sin arctan
s
2
p
s
2
p
q
x x
0
q
x x
0
2
2
2
2
ð
Þ
þ y y
0
ð
Þ
ð
Þ
þ y y
0
ð
Þ
15.3 Complex Analysis and Complex Potential
In MATLAB
both potential and streamfunction can be visualized more easily if
one adopts the notation of the 2D plane using
complex numbers
. The simplest
command sequence to produce a potential for a sink or source, are:
®
In Fig.
15.7
the real part of the logarithm is plotted. Compare with Fig. 14.1.
Instead of the computation of the real potential and the streamfunction, the
imaginary potential is evaluated. Real potential
'
, streamfunction
C
and imaginary
potential
F
are connected by the formula:
F ¼ ' þ iC
(15.10)
i
denotes the square root of -1, the imaginary unit. In MATLAB
®
specify the
imaginary number
z
by:
In the latter example the
real part
of z is -1, and the
imaginary part
is 2.
In MATLAB@ use the commands
real
and
imag
:
2
With
x
-component
Q
x
0
and
y
-component
Q
y
0
.
3
At position
ðx
well
; y
well
Þ
with pumping rate
Q.
4
At position
ðx
0
; y
0
Þ
with strength
A.
5
At position
ðx
0
; y
0
Þ
with strength
s
and angle
b.