Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
which is required to reach the user-specified length
L
.
M
denotes the number of
diffusion time steps necessary to fulfil the Neumann condition:
D
D
t
diff
D
x
2
1
2
Neu ¼
(4.9)
Note that in the m-file the time is specified explicitly, by a maximum simulation
time and an output time step. The algorithm is also described by Appelo and Postma
(
1993
).
4.3 Comparison Between Analytical and Numerical Solution
Compare analytical and numerical solutions, as obtained with the m-files
'analtrans.
m'
and
'simpletrans.m'
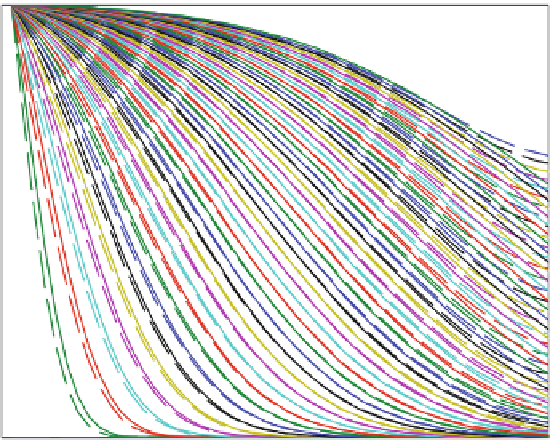
! A typical result is shown in Fig.
4.9
, which was obtained for
input values
T ¼
50. There
are differences at the start and the end of the simulation, while for intermediate times
the two curves coincide.
As was shown above the presented algorithm treats advection exactly to the
truncation error of numbers on the computer. The deviances between analytical and
numerical solutions are thus due to the discretization of diffusion. Directly after
start of the simulation the concentration gradient is very steep, and thus the error
1
; L ¼
1
; v ¼
1
; D ¼
0
:
1
; c
0
¼
0
; c
in
¼
1
; M ¼
50
; N ¼
1
dashed - num
solid - anal
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0
10
20
30
40
50
space
Fig. 4.9 Comparison of analytical and numerical results for the 1D transport equation