Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fixed bed
Fluidized bed
Pulverized fuel
Bubblling
Circulating
Heat transfer coeficient
Pressure loss
u
f
u
t
Gas velocity (m/s)
Particle velocity
Gas velocity
Slip
Increasing
particle load
Bed expansion
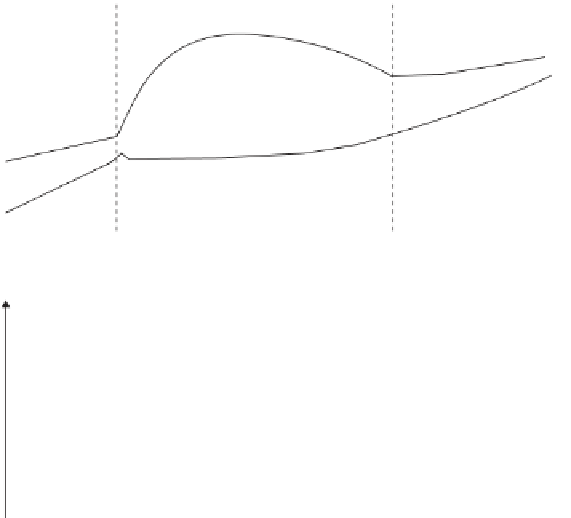
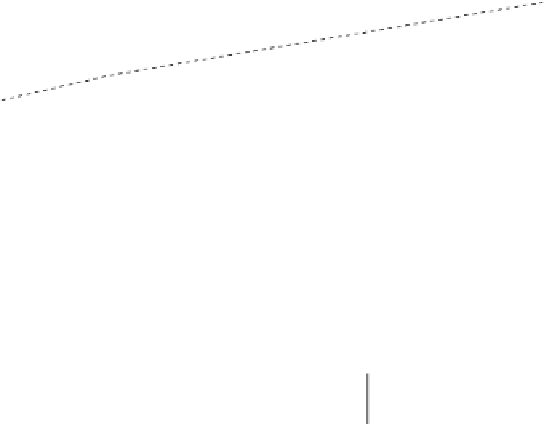
FIGURE 9.5
Distinctive features of different combustion systems.
Top: heat transfer
coefficient and pressure loss as a function of gas velocity. Bottom: velocity as a
function of the relative bed expansion
. (Source: Reproduced with permission from Görner
(1991). © Springer Science + Business Media.)
as well. In a bubbling fluidized bed (BFB), relatively low gas velocities are applied,
and consequently, only fine-grained ash is ejected from the fluidized bed after burnout
and abrasion of the solid fuel. Coarse-grained ash, however, accumulates in these
kinds of fluidized beds and, therefore, has to be removed. As a result of the higher
flow velocities of air and combustion gases in the circulating fluidized bed (CFB),







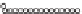

















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search