Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Δ{composition, temp., pressure,
pH, phase properties}
Δ{hydrodynamic flow regime}
Δ{time scales of production
and regeneration}
Operating conditions
Operating modes
Product(s)
Δ{composition, temp., pressure,
pH, phase properties}
Feed(s)
Process unit operation
Waste
Δ{composition, temp., pressure,
pH, phase properties}
Δ{safety, health and
environmental properties}
Availability
Δ{Reliability, maintainability}
Dynamics
Δ{response times, dyn. stability}
= tolerance window of variation of properties for feasible unit operation;
window = {properties}
nominal
± Δ{properties}
FIGURE 7.13
Windows of feasible operation of a processing technology.
1.
Chemical Species in Feeds and Products
First of all, the
items need to be considered: which species cannot
be tolerated at all by the specific processing technology? Such species are, e.g.,
specific catalyst poisons or aggressive chemicals that attack membrane or con-
tainment materials. Which changes in composition, temperature, pressure, and
pH can be tolerated? In case of multiphase streams, one needs tolerances with
respect to changes in phase ratio and the typical size of the dispersed phase
(droplets, bubbles, particles).
“
knockout
”
2.
Waste and SHE Aspects
Safety, health, and environmental (SHE) issues should be mentioned as well as
the expected variability in waste, both in quantity and quality.
3.
Operating Conditions
Concerning the internal physical state of the process unit, a process designer
needs to know the allowable ranges for temperature, pressure, and pH. For a mul-
tiphase system, the minimum and maximum phase ratios are required, as well as
the preferred hydrodynamic flow regime with restrictions to stay in that regime.
4.
Operating Modes
Many process units run in different operating modes over time, covering man-
ufacturing (either continuous or batchwise), regeneration of the active agents,
and cleaning. Designers need to know the lifetime expectancy of active agents
(e.g., catalysts) as well as the duration of nonmanufacturing modes, like regen-
eration and cleaning, with the associated procedures and means.







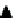




















Search WWH ::

Custom Search