Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
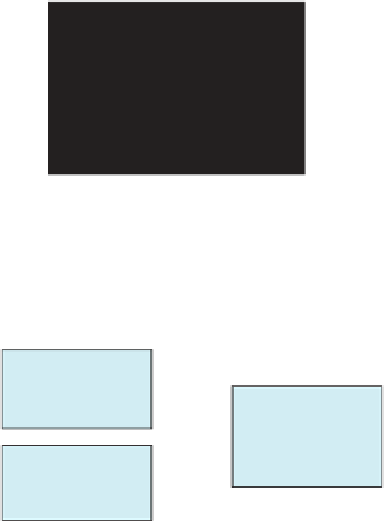
Input-output diagram of process
Preferred technologies
and license(s)
Process boundary
“battery limit”
Co-feed
Fuels
Oxygen
Biomass to energy
Heat
carrier
Reference
process
Power
Syngas
PROCESS
Biomass
Auxiliary
chemicals
(solvents, catalyst, etc.)
Wastes: G / L / S
Utility system
Syngas (1)
Co-feed
Fuels
Heat
Power
Subprocess 1
Oxygen
Subprocess 3
Subprocess 2
Syngas (2)
Biomass
FIGURE 7.8
Splitting a process into subprocesses.
3. Reversely, the intermediate product can be imported if the demand of sub-
process 3 exceeds the joint production capacity of subprocesses 1 and 2. In this
example, the syngas going to subprocess 3 is converted into three products:
liquid fuels, power, and heat.
d.
Analysis and (e) Evaluation
These are done for each alternative in the same way as for the full process, end-
ing with (f )
Selection
and (g)
Documentation
of the better options for propa-
gation to the next level of design.
7.8 PROCESS DESIGN: FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
Design at the third level generates a network of processing functions, encapsulated in
process units. The focus here is on which functions are needed and how they interact
in the network for an optimal performance. Targets are derived for the functional

















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search