Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
6.3 STEADY-STATE CONTINUOUS STIRRED TANK
REACTORS (CSTRs)
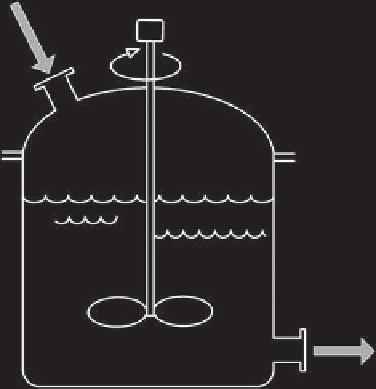
The continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR) is characterized by a continuous supply of
reactants and release of products (Figure 6.2). Like in the BR, the CSTR model works
under the assumption that the reactor is perfectly mixed, so the composition of the
mixture is exactly the same in the entire reaction volume. This type of reactor can
operate at steady or nonsteady state. In the steady state, which is the case considered
in this section, there are no dynamic variations in the inlet and outlet flows, and the
composition inside the reactor is constant. The temperature of the reaction mixture is
also constant, and the value should be such that the desired conversion and product
distribution are obtained. That temperature is kept constant by adjusting the amount of
heating or cooling of the system.
A material balance over the entire reactor for a reactant A is
Rate of accumulation = rate of supply
−
rate of release + rate of production
)
+V
0=
φ
n
,
A
0
−
φ
n
,
Af
=
φ
n
,
A
0
1
−
X
Af
R
ð Þ
−
ð
Eq
:
6
:
18
Þ
Note that since steady state is considered,
there are no time-dependent
terms.
Equation (6.18) can be rewritten as
V
φ
n
,
A
0
X
Af
−
=
ð
Eq
:
6
:
19
Þ
R
ð Þ
f
c
A0
φ
n
,
A
0
Feed
X
A
0=0
u
0
c
Af
=c
A
Products
φ
n
,
Af
=
φ
n
,
A
V, c
A
X
Af
=
X
A
(-
R
A
)
f
=(-
R
A
)
X
A
,
(-
R
A
)
u
f
FIGURE 6.2
Continuous stirred tank reactor.








Search WWH ::

Custom Search