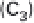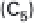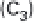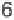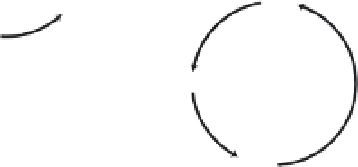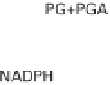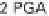Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
3.2 (a) Basic reactions of the photosynthetic carbon reduction
(Calvin) cycle (Smil 2002). (b) Dual role of Rubisco, as a
carboxylase in photosynthesis and as an oxygenase in photo-
respiration (based on Tolbert 1997).
pathway is made up of 13 enzyme-catalyzed reactions; its
three key sequences are carboxylation, reduction, and
regeneration.
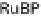
During carboxylation CO
2
(1-C compound) reacts
with the 5-C sugar ribulose-1-5-bisphosphate (RuBP) to
produce two molecules of 3-C PGA. The enzyme that
catalyzes this transformation is Rubisco, ribulose-1-5-
biphosphate carboxylase, a large water-soluble molecule
that makes up 16% of all protein in chloroplasts and
hence is the most abundant protein in the biosphere.
The resulting PGA is first phosphorylated with ATP
and then reduced, in a reaction using NADPH, to 3-
phosphoglyceraldehyde (PGAL, C
3
H
7
O
6
P), a 3-C (tri-
ose) sugar phosphate, the end product of the RPP cycle
(fig. 3.2). PGAL can be immediately metabolized in the
chloroplast or dimerized to produce stable 6-C sugars
(hexoses). Two of these sugars, fructose and glucose,
form a 12-C disaccharide sucrose. This is by far the most
important transport metabolite, the compound that
plants use to distribute most of their fixed carbon from
the leaves to be used by subsequent organic syntheses in
roots, stems, or flowers. Five out of every six molecules
of PGAL are converted, first to pentose phosphate, then
to ribulose-5-phosphate (R5P), whose phosphorylation
with ATP regenerates three molecules of RuBP, closing
and sustaining the cycle.