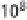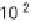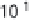Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
WW II, major subsidy, but because they are applied in
relatively small amounts, their high unit energy costs
(150-250 MJ/kg) do not add up to a high energy bur-
den. Higher crop yields are not a result of improved
photosynthesis. Photosynthetic rates are fixed, but new
high-yielding cultivars, especially short-stalked varieties of
wheat and rice, have much higher harvest indices (shares
of the photosynthate stored in the grain) than traditional
varieties, 45%-55% vs. 25%-30%, respectively. The new
cultivars respond vigorously to timely water, nutrient,
and pesticide applications, which reduce the amount of
photosynthate channeled into roots and into replacement
of damaged and destroyed tissues. But the peak national
harvests of staple cereals (@100 GJ/ha in terms of edible
grain) are still only a fraction of record yields.
Synthetic fertilizers account for slightly more than half
of all global farming energy subsidies, which prorate
from just a few GJ/ha in extensive cereal cropping to
about 10 GJ/ha in the United States, nearly 30 GJ/ha
in China, and 80 GJ/ha in Israel. The global total of
these energy subsidies (@13 EJ in 2000) has expanded
nearly 90-fold since 1900, and this has raised average
yields nearly fivefold, to more than 26 GJ/ha. Without
these subsidies global population would have to decline
even if the rich nations were to revert to largely vegetar-
ian diets. With the subsidies the world has a surplus of
agricultural production (daily average of about 18 MJ
per capita, compared to the minimum need of about 9
MJ). Food shortages and malnutrition are products of
unequal distribution and national mismanagement. Ris-
ing energy subsidies in farming released the rural labor
force to move into the growing manufacturing sector
and started a rapid transition to urban society, which is
now essentially complete in the rich countries.
13.7 Minimum cost of transport is calculated by dividing the
product of heterotrophic or machine mass (in kg), gravitational
constant, and optimum speed (in m/s) into the power input (in
W). Cost of flying is about 1 OM higher than that of land loco-
motion, and automobiles fit right along the line for large mam-
malian runners.
from CH
4
). The process was commercialized in 1913,
and its initially very high energy costs (
>
100 MJ/kg N)
were reduced by a series of innovations to less than 33
MJ/kg N by 2000. Nitrogen fertilizers subsequently
synthesized from ammonia cost 50-100 MJ/kg, and in-
tensive fertilizer applications represent embodied energy
costs of up to 40 GJ/ha.
Agricultural machinery is the third indispensable com-
ponent of farming energy subsidies. The first trial of a
gasoline tractor took place in 1892, and by 2000 there
were nearly 30 million of these machines worldwide,
averaging 30-50 kW (maxima @300 kW), costing 70-
120 MJ/kg to make and consuming 1.5-3.5 GJ/ha in a
variety of field operations. Pesticides are the latest, post-