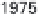Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
12.6 (
a
) Modern LNG tanker (photograph by Alstom Trans-
port). (
b
) Aggregate growth of global LNG fleet (based on a
graph in EIA 2004).
A rationally appraised technique should not be judged
unacceptable if its risks are several orders of magnitude
below those of natural disasters, yet the reverse is true
because of the fundamental divide in people's tolerance
of voluntary and involuntary exposures (Starr 1969;
Starr, Rudman, and Whipple 1976). People are willing
to assume voluntary risks about 3 OM higher than risks
from exposures perceived as involuntary, such as a nearby
siting of a nuclear power plant or an LNG terminal.
Natural mortality (the risk of dying is about 10
6
/
person
hour of exposure) acts as an important subcon-
scious yardstick in determining the acceptability of every-
day risks. Several voluntary activities (driving, commercial
flight) carry risks nearly as large as just living, but invol-
untary air pollution or radiation exposures, whose risks
are no higher than those of common natural hazards
(earthquakes, hurricanes, tornadoes), that is, 3-5 OM
lower than general disease mortality, are often seen as to-
tally unacceptable.
12.4 Energy and War
Wars demand an extraordinary mobilization of energy
resources, and modern wars, made possible by energy-
intensive weapons, represent the most concentrated and
the most devastating release of destructive power. In ad-
dition to casualties they bring major disruption of energy