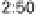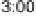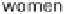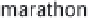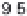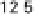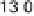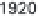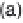Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
5.8
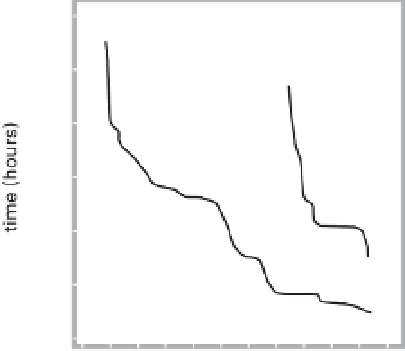
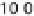
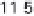
History of world records for the marathon and for 100 m.
Plotted from data in IAAF (2006).
is the fastest mode of human locomotion, and it has
energized all record-setting machines not only on land
but on water and in the air (D. G. Wilson 2004). Mon-
arch B completed a triangular 1.5-km course at nearly
10 m/sec (Drela and Langford 1985). Flying Fish II,a
watercraft with a hydrofoil ridden like a bicycle, outpaced
a single rower at about 6.5 m/s.
A healthy adult should tolerate many hours of work at
40%-50% of maximum aerobic capacity, equal (conserva-
tively) to gross metabolic power of 380-490 W for 60-
70-kg men. With typical kinetic efficiencies around 20%,
this would be 75-100 W of useful work. Measurements
in heavy manual occupations confirmed that 350 W of
total output are sustainable during an 8-h shift but rarely
exceeded. At 70 W the total daily useful work capacity is
just 2 MJ. That much kinetic energy can be liberated,
even when the conversion efficiency of an engine is a
mere 10%, by burning just 1 kg of ordinary steam coal
or 500 g of fuel oil. Human effort, even at its best, is a
most unimpressive source of mechanical energy.
Ultimately, the limits of human performance depend
on adequate food supplies. The body's carbohydrate
stores add up to a mere 400 g of glycogen in muscles,
100 g in the liver, and 3 g of glucose in the blood, a total
of just 8.4 MJ, good for a day's minimal survival needs.
Only 2-2.5 kg (33-42 MJ) of protein, or no more than
20%-25% of the body's total stores, can be metabolized
without endangering life; 30-50 days of minimum needs
would exhaust those reserves. Starving people must de-
rive most of their energy from fat. Between 2 kg and
3 kg of lipids are a structural part of cells, but the rest
(in adults 6-18 kg, or 226-678 MJ) can be converted
to last at least 40-50 days. Obese people would have
plenty of fat left for another month, but their protein
reserves would be gone. The range of starvation survival
is thus 4-8 weeks.