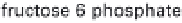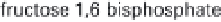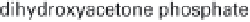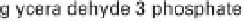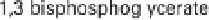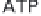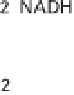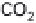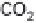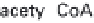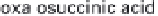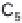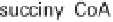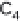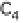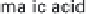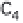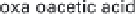Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
4.1
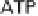
(a) Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway. (b) Krebs cycle.
W/g, 500 million times the Sun's rate. ATP-driven en-
ergy conversions in heterotrophs are no less awesome in
their intensity than the Sun's performance is in its overall
magnitude.
Basal metabolic rate (BMR) informs about the mini-
mum energy cost of steady-state existence, but it is not
easily determined because it must be measured at rest, in
a postabsorptive state, and in a thermoneutral environ-
ment. The most common approach to studying it across
the enormous variety of heterotrophic organisms has
been allometric scaling (Pedley 1977; McMahon and
Bonner 1983; Schmidt-Nielsen 1984; Brown and West
2000). The earliest scaling, based on just seven entries
for dogs (Rubner 1883), confirmed logical expectations
based on relations between BMR and body surface. A
body's mass and area are proportional, respectively, to
the cube and the square of a linear dimension: M zL
3
and AzL
2
; by rearrangement, AzM
2
=
3
. This means
that doubling a body's length increases its surface four-
fold and its volume eightfold. As the metabolic heat is