Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
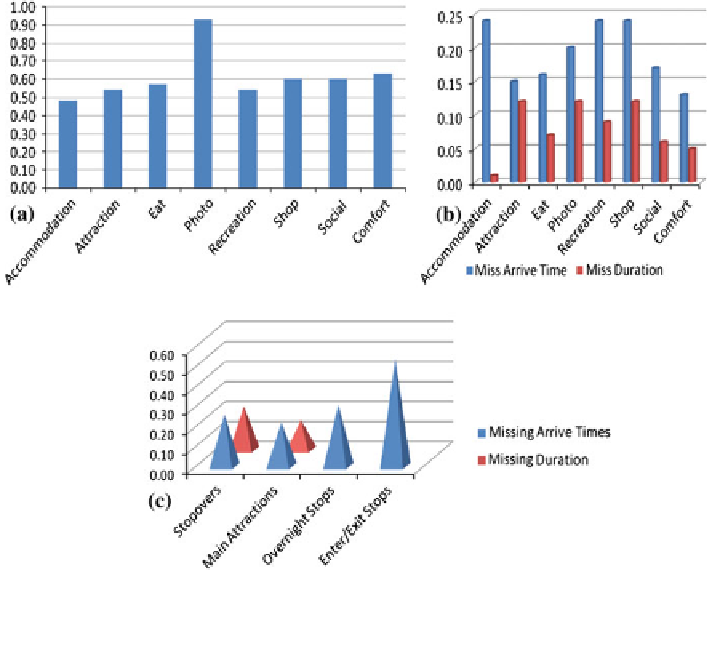
Fig. 8 a Percentage of completeness of temporal events by activities. b Percentage of arrival
time accuracy of temporal events by activities. c Percentage of comparison of missing temporal
events by types of stops
3.2.3 Patterns of Gaps and Errors by Activities
Analysis to date has identified some variations in data quality associated with
space and time. Activity at the stop and associated reasons for stopping, also have
a significant impact on people's memory and thus the reporting of spatiotemporal
survey data. Describing and coding activity was also an issue. In the original data,
tourists provided a free text response when asked for activity. Recoding required
close interpretation and in some cases a response was missing or uncodable.
In order to examine the data quality patterns associated with the activity data,
sample records were chosen and the recorded activities were grouped into eight
types as indicated in Fig.
8
a and
b
below.
One interpretation of Fig.
8
a is that different activities people chose left dif-
ferent impressions on people's memories. While mundane activities may leave
little impact pre-meditated activities with a high motivation factor may often
impact significantly and so have a clearer recollection of arrival times, particularly
if they have been driving towards a target arrival time as part of planning.
This may well be the case with itineraries planned prior to the holiday and so such
itineraries enjoy better completeness. Photographs may provide a further prompt