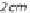Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Three- litre house -
A three-litre house colloquially is a house that requires around 3
litres of heating oil per square metre of living area per year (approx. 30 kWh) in Central
European climates. This corresponds to a primary energy requirement of around 60 kWh/
(m
2
a), which also includes the effi ciency of the heating system and hot water boiler.
Passive house -
A passive house can manage almost without any heating at all. The
annual heating requirement is less than 1.5 litres of heating oil (approx. 15 kWh) per
square metre of living area. This equates to a primary energy requirement of less than
40 kWh/(m
2
a).
Building insulation and window type have an important effect on heating require-
ments (Figure 3.7). The U-value is a comparison value for the quality of heat insula-
tion. This value indicates the heat loss per square metre of wall and window space
and per degree of temperature difference between indoors and outdoors. Low
U-values therefore mean low heat loss.
Figure 3.7
Effect of window type and insulation on heat loss.
Compared to non-insulated outer walls, walls with high-value heat insulation can
achieve a reduction of the U-value by more than a factor of 10 in an optimal case.
Conventional insulation against heat loss of around 20 cm would be required. This
is easily achievable with prefabricated houses using wood frame construction.
Vacuum-insulated materials with a thickness of around 2 cm that provides the same
insulation results have recently been developed. With this type of insulation a core
material of pyrogenic silicic acid is packed and evacuated into an airtight foil. It is
important that the special foil of the vacuum heat insulation prevents any air from
seeping in over long periods of time.