Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Wood pellet heating requires a very small investment of the user's time. The soot
and ash residue has to be cleaned out of the pellet boiler room every second month
or so. In addition, the ash pan should ideally be emptied once or twice a year. The
ash can be used as fertilizer in the garden.
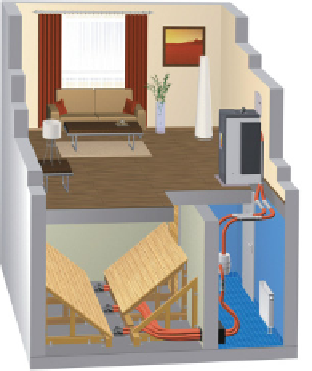
In addition to boilers designed for cellars, attractive pellet boilers are available for
use in living areas (Figure 12.10). These boilers can be installed in sitting rooms
and show a nice fl ame. Again, a suction device conveys the pellets from the store
that would still be located in the cellar.
Figure 12.10
Pellet boiler for living area use with pellet store in a cellar (left).
Source: Windhager
Zentralheizung.
12.3 Biomass Heat and Power Plants
In addition to being burnt in stoves and boilers for heating systems in single homes
and apartment blocks, biomass can also be used in large heat plants. A central heat
plant consists of a high-performance boiler and a fuel store. The fuel store is usually
big enough to ensure that independent operation can be guaranteed for several days
or even weeks. A district heating grid then transports the heat to the consumers
connected to the grid (Figure 12.11).
With centralized heat plants, individual consumers no longer have to worry about
fuel procurement and system maintenance. These tasks are handled by the operator
of the heat plant. The effi ciency of large heat plants is often somewhat higher than
that of small non-central systems. On the other hand, heat losses are higher because
of the long pipes in the district heating grid. However, large heat plants fare con-
siderably better when it comes to the emission of harmful substances. Compared to
heating systems in single-family homes, large plants use more modern fi ltering