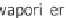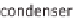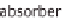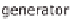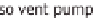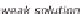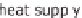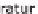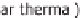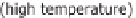Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
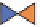
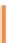
Figure 11.4
Principle of absorption heat pumps.
The function of a thermal compressor is to compress and heat the refrigerant. This
happens through a chemical process of sorption, for example through the dissolving
of ammonia in water. This was explained in the section 'Cooling with the sun' in
Chapter 6. The heat released through sorption can be used as thermal heat.
A solvent pump transports the solution to the generator. The solvent pump, unlike the
compression heat pump, does not build up high pressure, so a relatively low amount of
electrically driven energy is needed. The generator now has to separate the water and
refrigerant ammonia in the solution again to enable the sorption to take place once more.
High temperature heat is needed for the expulsion. Solar heat and biogas can be used.
The high temperature heat supplied is well below the dissipated quantity of useful
heat. The main advantage of absorption heat pumps is that they use a very small
amount of valuable electric energy. They are particularly useful for large-scale
applications. They are also used as refrigerating machines in refrigerators run with
propane gas. The refrigerant ammonia is toxic and fl ammable. However, it is a
widely used chemical and is considered easy to control.
Adsorption heat pumps, which only differ by two letters from absorption heat
pumps, likewise use thermal energy as the driving energy.
What is meant by adsorption is that a gas like water vapour is added to a solid
material, such as active coal, silica gel or zeolite. The process of adsorption, thus
the bonding of the water vapour through the solid material, creates high tempera-
tures that can be utilized by a heat pump. However, adsorption heat pumps are still
at the research stage and therefore will not be covered in detail in this topic.
11.3 Planning and Design
Today heat pumps are available for almost any heat capacity desired. Manufacturers
usually provide advice on selection and design. The most important aspect in plan-
ning is the selection of a low temperature heat source and how to exploit it.