Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
■
Hot steam deposits
■
Thermal water deposits
■
HDR (hot dry rock)
Hot steam and thermal water sources can be used directly for heating purposes or
to generate electricity. If the underground consists only of hot rock, this can heat
up cold water that is compressed into the depth.
10.2 Geothermal Heat and Power Plants
10.2.1 Geothermal Heat Plants
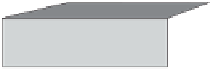
If boreholes already exist in a thermal water area, it is comparatively easy to develop
a geothermal heat supply. In geothermal heat plants a feed pump fetches hot thermal
water from a production well to the surface (Figure 10.6). As thermal water often
has a high salt content, along with certain natural radioactive impurities, it cannot
be used directly to provide heat. A heat exchanger extracts the heat from the thermal
water and transfers it to a district heating grid. A reinjection well injects the cooled
thermal water back into the earth.
Figure 10.6
Principle of
a geothermal heat plant.
Relatively low temperatures of 100 °C or less are suffi cient for heating purposes.
Deep drilling depths are therefore not necessary.