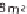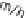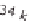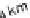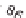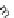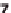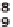Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Wind Power
For a specifi c wind velocity
v
, the power of the wind
P
wind
is calculated by the area
A
for air density
ρ
1
2
P
wind
=⋅
ρ
⋅
A v
⋅
3
With a wind velocity of 2.8 metres per second (m/s), which equates to 10 km/h or
6.2 mph, the wind with an air density of
ρ
= 1.225 kg/m
3
on an area of 1 m
2
only
reaches a relatively low capacity of
3
1
2
kg
m
m
s
⋅
⎛
⎞
⎟
=
P
wind
=⋅
1 225
.
⋅
1
m
2
2 8
.
13 4
.
W.
⎜
3
With a wind velocity of 27.8 m/s, thus 100 km/h or 62.1 mph, the capacity rises a
thousandfold and reaches 13.2 kW, which corresponds to around 18 PS (Figure 8.4).
Figure 8.4
Area through which the wind reaches a capacity of 100 kilowatts at different
wind speeds.
Meteorology still follows the practice of indicating wind velocity
v
based on the
Beaufort scale (bft). The 12-level Beaufort scale was developed by the British
Admiral Sir Francis Beaufort, who observed the sail behaviour of a naval frigate in
different wind conditions and categorized it into different levels in 1806. The British
navy offi cially introduced the Beaufort scale in 1838 (Table 8.1).