Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
improvements in effi ciency are needed in this area. Concentrator cells in which
sunlight is concentrated through mirrors or lenses reach a very high effi ciency but
are considerably more expensive than normal silicon cells.
In addition to effi ciency, there are other parameters that describe photovoltaic
modules. The current-voltage characteristic is usually found in relevant data sheets.
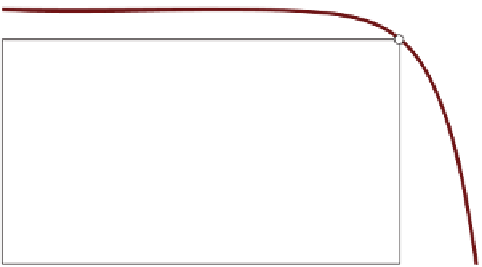
The maximum current
I
SC
fl ows with a short-circuited photovoltaic module. The
short-circuiting is not dangerous to the module. The short-circuit current is limited
and depends on the solar radiation intensity. If nothing is connected to the photo-
voltaic module, it is in open circuit and no electricity fl ows. It then adjusts itself to
the open-circuit voltage
V
OC
. A photovoltaic module is unable to produce any power
when in short circuit or open circuit. Between open circuit and short circuit the
current depends on the voltage. The principal process of the curve is similar for all
solar modules (Figure 5.3 and Table 5.2 ).
maximum power
point MPP
I
SC
I
MPP
photovoltaic power
P
MPP
=
V
MPP
·
I
MPP
V
MPP
V
OC
photovoltaic voltage
V
Figure 5.3
Current-voltage curve for a photovoltaic module.
In practice, the aim is to take maximum power from the photovoltaic module. This
corresponds to the largest rectangle that can be slid under the curve. The top edge
on the right of the rectangle on the curve is called the MPP (maximum power point).
The voltage that belongs to the MPP is called MPP voltage, in short
V
MPP
. A pho-
tovoltaic module provides maximum power with this voltage. In practice, operation
close to that of the MPP can be achieved, for example when a battery with voltage
close to that of the MMP voltage is connected or where an inverter automatically
adjusts the MMP voltage on the photovoltaic module.
The current of photovoltaic modules, and hence the power, drops according to the
number of incoming photons, and thus the radiation intensity of the sunlight. If the
solar radiation intensity is halved, then the power of the photovoltaic modules is
also reduced by half. The power of photovoltaic modules also drops with high
temperatures. If the temperature rises by 25 °C, the power of the crystalline solar
cells falls by about 10%. Therefore, when photovoltaic modules are installed, care
should be taken that they are always well ventilated and a draught cools the modules
(Table 5.2 ).