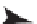Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Resident
predators &
parasitoids
Transient
coccinellids
IGP
*
***
**
Soybean
aphid
***
Soybean
Figure 8.6
. Summary of tri-trophic level interactions in the soybean aphid system.
Thickness and direction of lines indicate the magnitude and direction of impacts. Dashed
lines represent potential interactions that have not yet been shown to occur and asterisks
represent increasing levels of statistical significance (P = 0.05 - 0.001). IGP = intraguild
predation. Based on Costamagna and Landis (2006), Costamagna et al. (2007a, b, c; 2008),
and Gardiner and Landis (2007).
their competitors—appears to be limiting the impacts of the parasitoid community
(Costamagna and Landis 2006).
Intraguild Predation
In subsequent studies conducted at the KBS LTER Biodiversity Gradient
Experiment (Robertson and Hamilton 2015, Chapter 1 in this volume) and other
locales, Costamagna et al. (2008) explored the role of intraguild predation between
generalist predators and parasitoids. In addition, they examined the potential for
the community of natural enemies to cause a trophic cascade (Costamagna et al.
2007a). They used selective exclusion cages that allowed the exploration of how the
soybean aphid was impacted by parasitoids (in the absence of most predators) and
by the presence of both predators and parasitoids. Results demonstrated the poten-
tial for season-long suppression of soybean aphid by the community of generalist
natural enemies and a resulting trophic cascade, leading to increased soybean yield.
In both studies, parasitoids alone provided statistically significant but biologically
modest suppression of soybean aphid populations; they delayed peak aphid popu-
lations but not for long enough to suppress populations below their threshold for
economic harm.