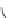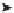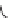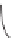Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Plant
Biomass
soil surface
belowground
Structural C
Metabolic C
Structural C
Metabolic C
CO
2
Microbial C
Microbial C
CO
2
CO
2
CO
2
Slow
Organic C
CO
2
CO
2
CO
2
CO
2
Passive
Organic C
Figure 6.6
. The soil subsystem of the Century Model (Parton et al. 1987) includes micro-
bial transformations of plant biomass where assimilated carbon is apportioned between car-
bon dioxide (CO
2
) and microbial biomass both at the soil surface and belowground. In both
cases, the model assumes that 55% of the carbon assimilated by microbes is oxidized to CO
2
with the remainder incorporated into cell biomass, which is equivalent to a bacterial growth
efficiency of 0.45.
cell biomass. This assumption has profound consequences for the predicted fate
of C, including its retention in soil and the potential for global-scale feedbacks.
While the assumption that 55% of the C metabolized by microbes is released
as CO
2
may be reasonable for pure cultures provided with substrates and nutri-
ents in optimal proportions, the proportion of carbon respired to CO
2
changes
under substrate or nutrient limitation (del Giorgio and Cole 1998). The effi-
ciency by which microbial communities use resources to produce more biomass
is not determined by a single enzyme or pathway, as the assumption implies, but
rather by their ability to coordinate cellular activity with environmental signals.
The net result of this integrated cellular system is a balance between growth
and respiration that is characteristic of each microbe. To understand the rate
and controls of microbial transformations of C in soil, we need to advance our
knowledge of the processes that influence C metabolism in different members
of the community. In other words, it is critical that we better understand the
fundamental physiological and ecological mechanisms that control the assimila-
tion and fate of C processed by soil microbes. Studies of microbial populations
in KBS LTER soils are contributing to this understanding and are the subject of
the next section.