Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
When landfill is full,
layers of soil and clay
seal in trash
Topsoil
Electricity
generator
building
Sand
Clay
Methane storage
and compressor
building
Garbage
Leachate
treatment system
Probes to
detect
methane
leaks
Pipes collect explosive
methane as used as fuel
to generate eleectricity
Methane gas
recovery well
Leachate
storage
tank
Compacted
solid waste
Groundwater
monitoring
well
Leachate
pipes
Leachate pumped
up to storage tank
for safe disposal
Garbage
Sand
Synthetic
liner
Sand
Leachate
monitoring
well
Groundwater
Clay and plastic lining
to prevent leaks; pipes
collect leachate from
bottom of landfill
Clay
Subsoil
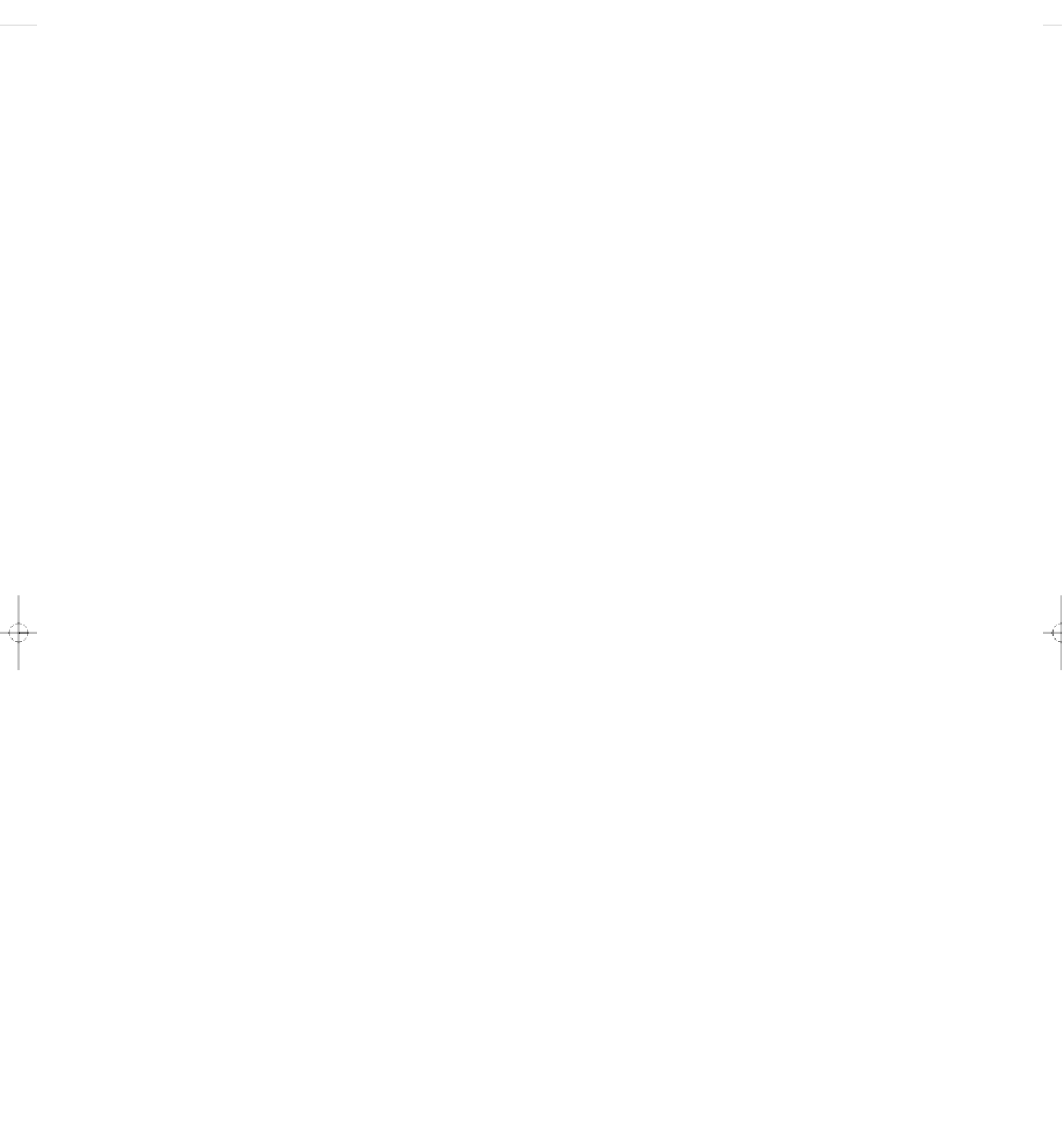
Figure 17-11
Solutions:
state-of-the-art
sanitary landfill,
which is designed to eliminate or minimize environ-
mental problems that plague older landfills. Even these landfills are expected to leak eventually, passing both
the effects of contamination and the cleanup costs on to future generations. Since 1997, only sanitary landfills
have been able to operate in the United States. As a result, many older and small landfills have been closed
and replaced with larger local and regional modern landfills.
before being filled with garbage, as shown in Fig-
ure 17-11. The landfill bottom is covered with a second
impermeable liner, usually made of several layers of
clay, thick plastic, and sand. This liner collects
leachate
(rainwater contaminated as it percolates through the
solid waste) and is intended to prevent its leakage into
groundwater. Wells are drilled around the landfill to
monitor any leakage.
The leachate is pumped from the bottom of the
landfill, stored in tanks, and sent to a regular sewage
treatment plant or an on-site treatment plant. When it
becomes full, the landfill is covered with clay, sand,
gravel, and topsoil to prevent water from seeping in.
Sanitary landfills have a network of vent pipes to
collect landfill gases (consisting mostly of two green-
house gases, methane and carbon dioxide) released by
the underground decomposition of wastes. The
methane is filtered out and burned in small gas tur-
bines to produce steam or electricity for nearby facili-
ties or sold to utilities for use as a fuel.