Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Electricity
Smokestack
W
a
ste
pi
t
W
ate
r
ad
de
d
D
irty
w
ate
r
B
ott
om
as
h
C
on
vey
or
F
ly a
sh
Conventional
landfill
Waste
treatment
Hazardous
waste landfill
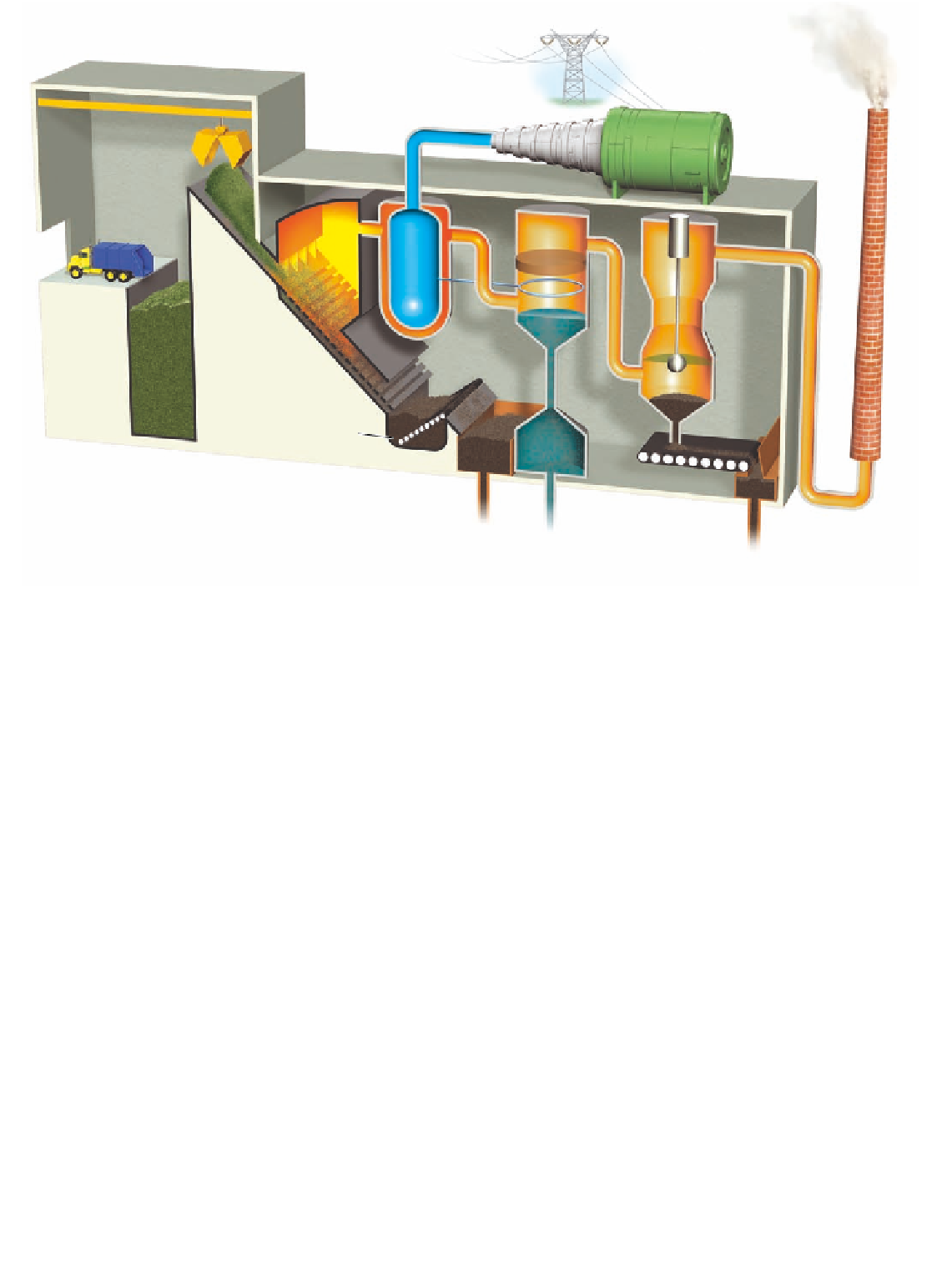
Figure 17-9
Solutions:
this
waste-to-energy incinerator
with pollution controls burns mixed solid waste and
recovers some of the energy to produce steam used for heating or producing electricity. (Adapted from U.S.
Environmental Protection Agency,
Let's Reduce and Recycle
)
T rade-Offs
Science: Burying Solid Waste
Most of the world's municipal solid waste is buried in
landfills that will eventually leak toxic liquids into the
soil and underlying aquifers.
About 54% by weight of the MSW in the United States
is buried in sanitary landfills, compared to 90% in the
United Kingdom, 80% in Canada, 15% in Japan, and
12% in Switzerland. Two types of landfills exist.
Open dumps
are essentially fields or holes in
the ground where garbage is deposited and some-
times covered with soil. They are rare in developed
countries, but are widely used in many developing
countries, especially to handle wastes from megacities.
Thousands of people—including many children—
work and live in such open dumps or spend time there
looking for food scraps and reusable and recyclable
items (Figure 17-6).
In newer landfills, called
sanitary landfills,
solid
wastes are spread out in thin layers, compacted, and
covered daily with a fresh layer of clay or plastic foam.
State-of-the-art landfills located on geologically suit-
able sites and away from lakes, rivers, floodplains, and
aquifer recharge zones are lined with clay and plastic
Incineration
Advantages
Disadvantages
Reduced trash
volume
High cost
Air pollution
(especially
toxic dioxins)
Less need for
landfills
Produces a
highly toxic ash
Low water
pollution
Encourages
waste production
Quick and
easy
Discourages
recycling and waste
reduction
Figure 17-10
Trade-offs:
advantages and disadvantages
of incinerating solid waste. These trade-offs also apply to the
incineration of hazardous waste.
Critical thinking: pick the
single advantage and disadvantage that you think are the most
important.