Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
of their high costs, the limited number of suitable sites,
and availability of much cheaper ways to produce
electricity such as combined-cycle natural gas turbines
and wind turbines.
On an individual scale, inexpensive
solar cookers
can focus and concentrate sunlight to cook food, espe-
cially in rural villages in sunny developing countries.
They can be made by fitting an insulated box big
enough to hold three or four pots with a transparent,
removable top. Solar cookers reduce deforestation for
fuelwood as well as the time and labor needed to col-
lect firewood. They also reduce indoor air pollution
from smoky fires.
T rade-Offs
Solar Energy for High-Temperature
Heat and Electricity
Advantages
Disadvantages
Moderate net
energy
Low efficiency
High costs
Moderate
environmental
impact
Needs backup or
storage system
No CO
2
emissions
Need access to
sun most of
the time
Fast construction
(1-2 years)
Science: Producing Electricity
with Solar Cells
Solar cells that convert sunlight to electricity can be
incorporated into roofing materials or windows, and
the currently high costs of doing so are expected to fall.
Solar energy can be converted directly into electrical
energy by
photovoltaic (PV) cells,
commonly called
solar cells
(Figure 13-33). A typical solar cell is a trans-
parent wafer that contains a semiconductor with a
thickness ranging from less than that of a human hair
to a sheet of paper. Sunlight energizes and causes elec-
trons in the semiconductor to flow, creating an electri-
cal current. These devices have no moving parts, re-
quire little maintenance, produce no pollution during
operation, and last as long as a conventional fossil fuel
or nuclear power plant. The semiconductor material
High land use
Costs reduced
with natural gas
turbine backup
May disturb
desert areas
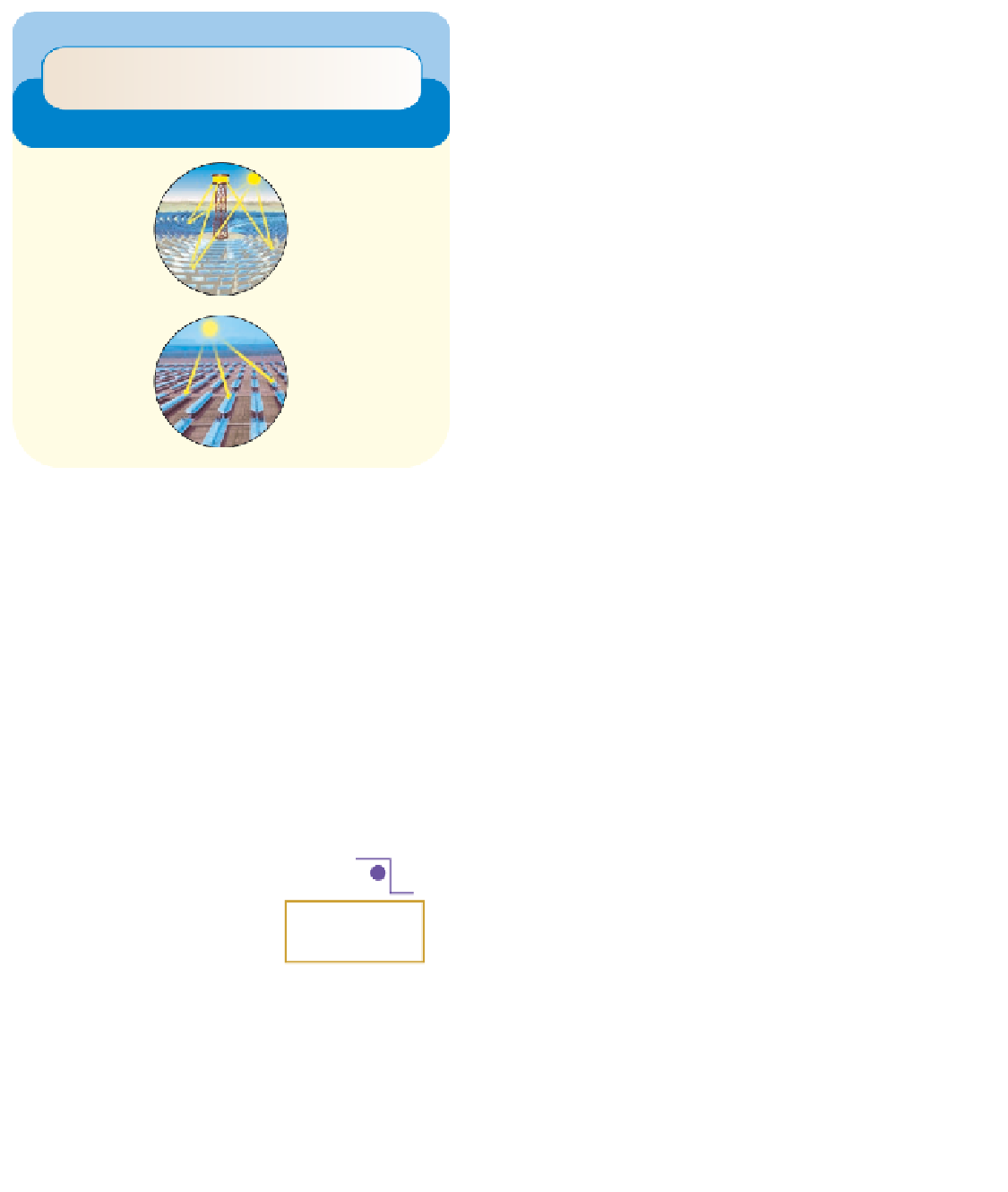
Figure 13-32
Trade-offs:
advantages and disadvantages of
using solar energy to generate high-temperature heat and elec-
tricity.
Critical thinking: pick the single advantage and the single
disadvantage that you think are the most important.
generating electricity. At night or on cloudy days,
high-efficiency, combined-cycle, natural gas turbines
can supply backup electricity as needed.
Most analysts do not expect widespread use of
such technologies over the next few decades because
Single solar cell
Solar-cell roof
-
Boron-
enriched
silicon
+
Junction
Roof options
Panels of solar cells
Phosphorus-
enriched silicon
Solar shingles
Figure 13-33
Solutions:
photovoltaic (PV) cells can provide electricity for a house or building using solar-cell
roof shingles, as shown in the house on the right in Richmond, Surrey, England. PV panel roof systems that look
like a metal roof are also available. In addition, new thin-film solar cells can be applied to windows and outside
glass walls.