Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
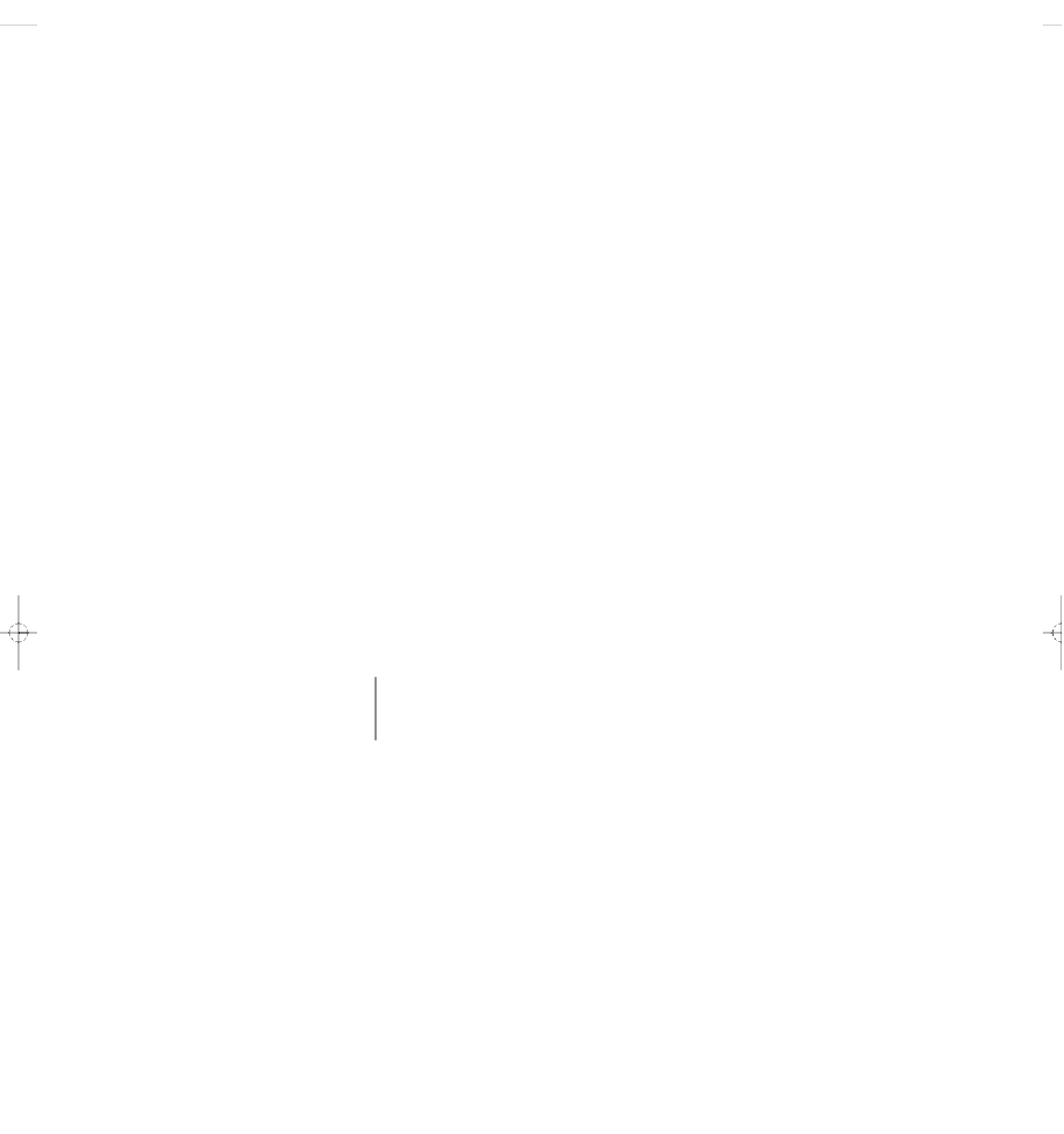
Oil and natural gas
Floating oil drilling platform
Oil storage
Coal
Contour
strip mining
Geothermal energy
Oil drilling
platform
on legs
Hot water storage
Geothermal
power plant
Oil well
Pipeline
Gas well
Valves
Mined coal
Area strip
mining
Pump
Pipeline
Drilling
tower
Coal seam
Water penetrates
down through
the rock
Figure 13-2
Natural capital:
important nonrenewable energy resources that
can be removed from the earth's crust are coal, oil, natural gas, and some
forms of geothermal energy. Nonrenewable uranium ore is also extracted from
the earth's crust and then processed to increase its concentration of uranium-
235, which can serve as a fuel in nuclear reactors to produce electricity.
Nuclear power
6%
Nuclear power
8%
Hydropower, geothermal,
solar, wind
7%
Hydropower
geothermal,
solar, wind
3%
,
Natural
gas
23%
Natural
gas
21%
Biomass
11%
Coal
23%
Coal
22%
Biomass
4%
Oil
33%
Oil
39%
World
United States
Figure 13-3
Natural capital:
commercial energy use by source for the world (left) and the United States (right)
in 2003. Commercial energy amounts to only 1% of the energy used in the world; the other 99% is direct solar
energy received from the sun and is not sold in the marketplace. (Data from U.S. Department of Energy, British
Petroleum, Worldwatch Institute, and International Energy Agency)