Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
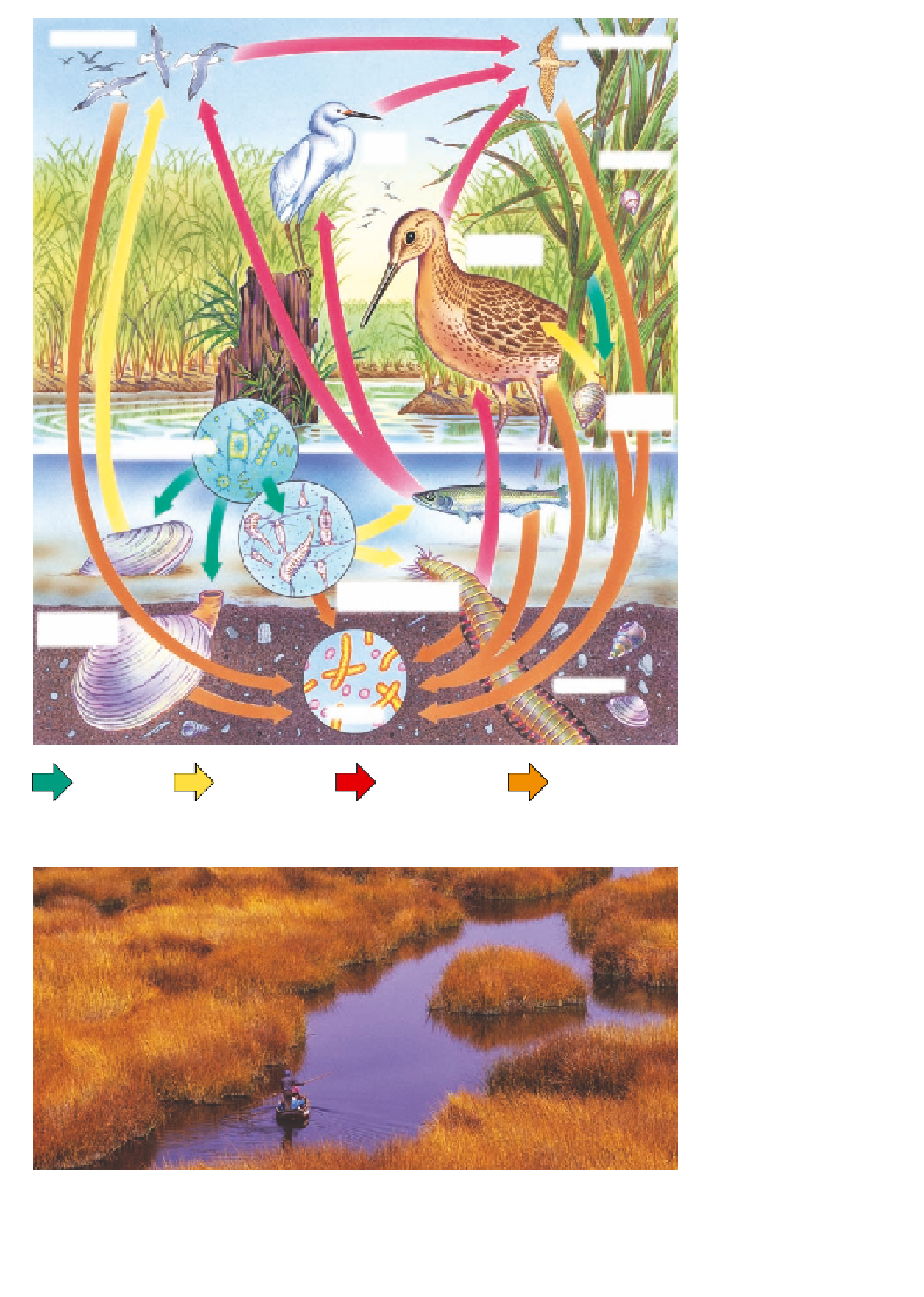
Herring gulls
Herring gulls
Peregrine falcon
Peregrine falcon
Snowy
egret
Snowy
egret
Cordgrass
Cordgrass
Short-billed
dowitcher
Short-billed
dowitcher
Marsh
periwinkle
Marsh
periwinkle
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton
Smelt
Smelt
Zooplankton and
small crustaceans
Zooplankton and
small crustaceans
Soft-shelled
clam
Soft-shelled
clam
Clamworm
Clamworm
Bacteria
Bacteria
Producer to
primary
consumer
Primary to
secondary
consumer
Secondary to
higher-level
consumer
All consumer
and producers
to decomposers
Figure 5-28
Natural capital:
components and interactions in a
salt marsh ecosystem
in a tem-
perate area such as the United States. When these organisms die, decomposers break down
their organic matter into minerals used by plants. Colored arrows indicate transfers of matter and
energy between consumers (herbivores); secondary, or higher-level, consumers (carnivores);
and decomposers. Organisms are not drawn to scale. The photo shows a salt marsh in Peru.