Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
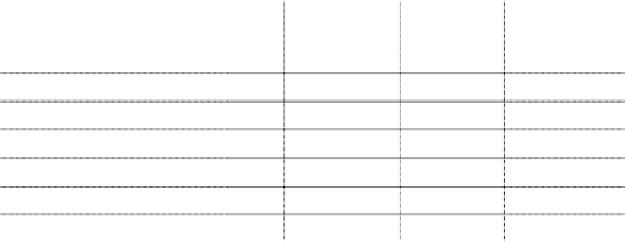
Table 12.
Paiwise comparison of criteria weights (2
nd
level of tree) and respective Priority
Vector (calculated)
Criteria Weights
Contribution
Stakeholders Importance
Priority Vector
Contribution
1.000
0.500
0.333
Stakeholder Importance
2.000
1.000
0.667
alternatives by means of pairwise comparisons, for example by deriving relative
weights from different comparisons. This would reduce the number of comparisons to
n-1
; however, if an error is introduced in this process, a strong negative impact can be
felt in the final result [21, p. 86]. Fortunately, there are commercial tools, such as
Expert Choice, Rank Master and Descriptor, to support the AHP process, facilitating
its use and speeding up the calculations.
Step 4: Synthesis
After creating all pairwise comparisons it is now possible to calculate the priority of
each alternative in terms of each criterion. First we calculate the normalized pairwise
comparison matrix by dividing each element of the comparison matrix by the sum of
each column. Then we find the estimated relative priorities by calculating the average
of each row of the normalized matrix. At the end of this step we have the priority
vectors for each pairwise matrix. Second, we collect the priority vectors for the third
level of matrix in one matrix and using the importance priority vector (Table 11) we
calculate the synthesized value for level 3. Table 12 shows the intermediate collected
vectors and the final priority vector for level 3.
Now, to calculate the final ranking, we need to combine, into a single matrix, the
final priority vector determined in Table 13 with the final vector resulting from
Table 7, and then multiply it by the criteria weights priority vector of level 2 (Table
12). The results are shown in Table 14.
Observe that, in our example, we only have two major criteria at level 2 and three
sub-criteria at level 3 (Fig. 4); hence, the final ranking was obtained by first
synthesizing level 3 (Table 13) and then synthesizing level 2 (Table 14). As
mentioned before, the AHP works with a bottom-up approach.
Table 13.
Priority matrix for level 3 plus final Vector
Passenger
Importance
System Owner
Importance
Developer
Importance Priority Vector
0.093
0.178
0.146
0.155
Accuracy
Response Time
0.478
0.196
0.146
0.227
Availability
0.114
0.149
0.186
0.154
Integrity
0.067
0.091
0.113
0.093
Multi-Access
0.123
0.178
0.172
0.167
Validate Card
0.088
0.138
0.172
0.1408
Fault Tolerance
0.038
0.071
0.065
0.064






























Search WWH ::

Custom Search