Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
DM1 tries to exploit the improved consciousness about the objective levels that can be
actually achieved, and fixes a new reference variation for the objective 2. This kind of
behaviour continues until the iteration 4. As a matter of fact, this last iteration is considered a
worsening by DM1 and, also in view of other steps, DM1 feels quite satisfied with the
solution given by iteration 4. To transform the subjective satisfaction into an objective
evaluation of the quality of the solution is quite a hard task in a multi-objective problem. In
the proposed decision problem, where the objectives are normalized, a star coordinate system
representation may help both the DM to view the solution with respect to the reference, the
nadir and the utopia points, and the DSS specialist to have a more objective evaluation of the
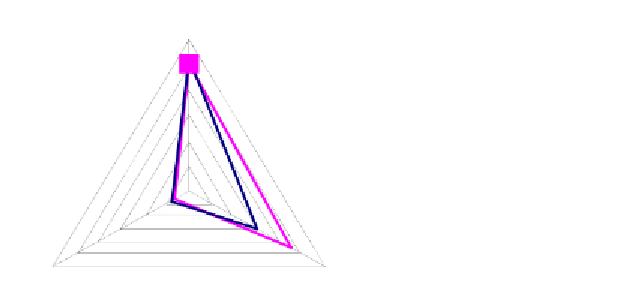
quality of results. Figure 2 shows the solution at the iteration 4 and the related reference
point; the nadir coordinates are the end points of the star, whereas the utopia ones are in the
centre of the star. The solution can be assessed as adequate also since it is almost included in
the area delimited by the convex hull of the reference points and because its objectives are
lower than the mean of the solutions obtained.
1
0,6
0,5
0,4
0,3
Ref er ence
Point
0,2
0,1
0
Obj ec t i v e
values
3
2
Figure 3.2. The star representation of the result of the iteration process for DM1.
A similar process characterizes the iterations performed by DM2. However in this case,
the behavior of DM2 in the decision process has some important differences with respect to
DM1. While DM1 has started from the unfeasible utopia as reference point, DM2, who shows
some awareness about the possible outcomes that one can expect for the considered MSW
management problem, starts from a reference point that, satisfying all the problem
constraints, results to be feasible. The attitude by DM2 in the iterations of decision algorithm
is different with respect to DM1. While DM1 relaxed the reference point according to ideas
suggested from the solution obtained in the current iteration, DM2 needs to firm up on
improving the amount of recycled waste (objective
q
2
), taking into account the effects on the
other objectives.
The iteration of the decision process is summarized by the values in the table 3.3.
Moving from iteration 1 to 2,
q
1
and
q
3
remain the same while
q
2
is lowered and
q
4
is
increased. From iteration 2 to 3,
q
1
rises while the other objectives decrease. However, DM2
is not very satisfied by
q
1
and wants to lower it. At iteration 4,
q
1
is lowered, and
q
2
and
q
3
increase a bit. DM2 is satisfied by this iteration. Figure 3.3 reports the star representation for
the result of the DM2 iteration process.













Search WWH ::

Custom Search