Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Bulk Gas Analytical Method
The bulk gas analysis determines total compositions of fluid released from whole liquid-
rich inclusions in each sample of about 0.3 g decrepitated during heating to 500 ºC within a
few minute. If one inclusion in large size is contained in the whole inclusions decrepitated,
the bulk gas composition not always indicates mean value of whole inclusions because of
significantly affected large inclusions. The gases released by decrepitation were collected in
the stainless steel tubing. The gas pressure was measured by the capacitance manometer after
separating the water with a cold trap to obtain the gas/water ratio. Ion counts were measured
by QMS for each gas species except H
2
O and converted to pressure. Calibrations were
conducted using standards for CO
2
, CH
4
, N
2
and Ar. Quantification of reactive gases such as
H
2
S and SO
2
was not successful owing to the adsorption and reaction of these gases with the
stainless steel tubing. Experimental precision is estimated to be better than 10 % for each of
the gas species.
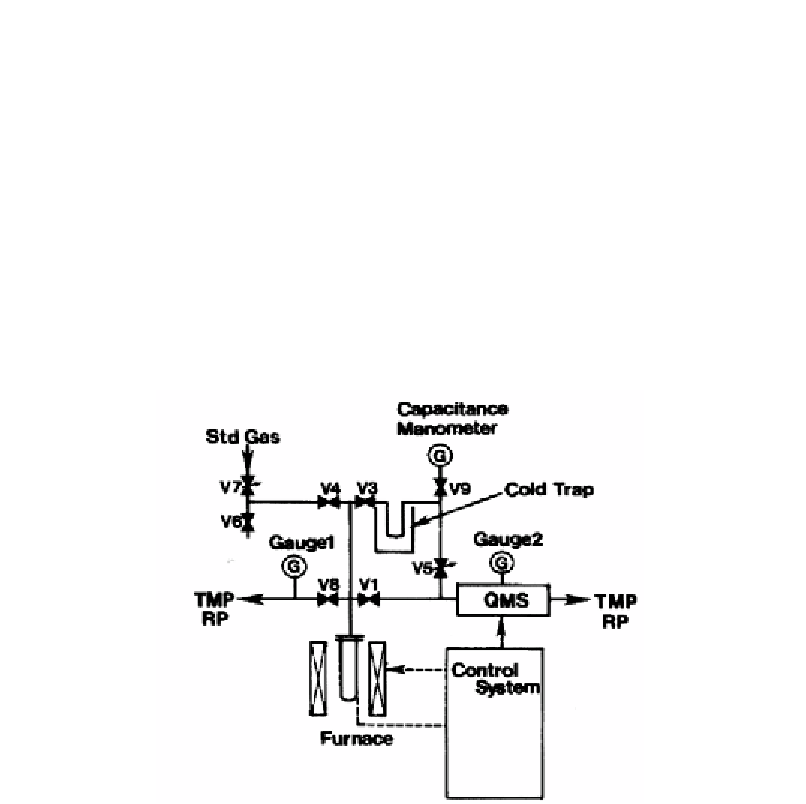
Figure 7. Equipment for fluid inclusion gas analysis (Sasada et al., 1992). Gauges 1 and 2, ionization
gauges; V1-V4, V6, V8 and V9, bellows valve; V5 and V7, leak valve; TMP, turbomolecular pump;
RP, rotary pump; QMS, quadrupole mass spectrometer.
3.2.2. Interpretation of Gas Analytical Data
Individual Gas Analytical Data
The gas analytical chart of individual liquid-rich inclusion trapped a liquid homogeneously
in anhydrite from the Matsukawa geothermal field is shown in figure 8A.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search