Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
measurement with an ordinary three electrode system. There has been only one report [29]
that used agarose gel (1 wt%) for an electrochemical measurement; in this report only a gold
wire working electrode was used, and a much lower diffusion coefficient of ferricyanide
(1/2.6) in the agarose gel was obtained compared to that in an aqueous solution. If
electrochemical measurements using ordinary electrodes could be carried out in a solid
medium in the same way as in a pure liquid, a new kind electrochemistry and electrochemical
measurements could be initiated.
In the present section 3, tight and elastic polysaccharide solids were used as solid
electrolyte media for very conventional three electrode electrochemical measurements. The
fundamental electrochemical properties of the polysaccharide solid were investigated by
electrochemical impedance spectroscopy including diffusion of redox molecules, charge
transfer resistance at the electrode|solid interface, and double layer capacitance on the
electrode surface.
Electrochemical Characteristics in Polysaccharide Solid Media
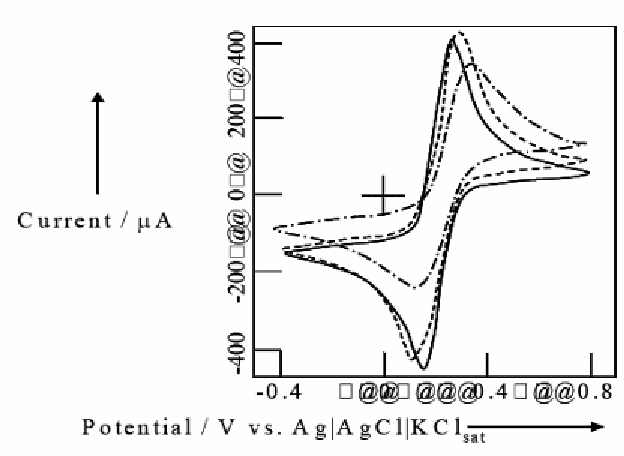
Cyclic voltammograms of 5 mM Fe(CN)
6
3-
in a 2 wt% agarose solid, in a 2 wt% κ-
carrageenan solid, and in an aqueous solution containing 0.5 M KCl are shown in figure 4.
Figure 4. Cyclic voltammograms of 5 mM Fe(CN)
6
3-
in 2 wt% agarose (dash-dotted line) [3]; 2 wt% κ-
carrageenan (dashed line) and aqueous solution (solid line) containing 0.5 M KCl in the range from -
0.4 to 0.8 V (vs. Ag|AgCl|KCl
sat
). Working electrode is ITO, and counter electrode Pt. Scan rate, 20 mV
s
-1
.
The voltammograms in the agarose andκ-carrageenan solids show very similar features as
in liquid water including the redox potential, and peak currents, but with a slightly larger peak
separation for the solid systems. The solid was so tight and stable that CV could be measured
without any outer cell or vessel.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search