Database Reference
In-Depth Information
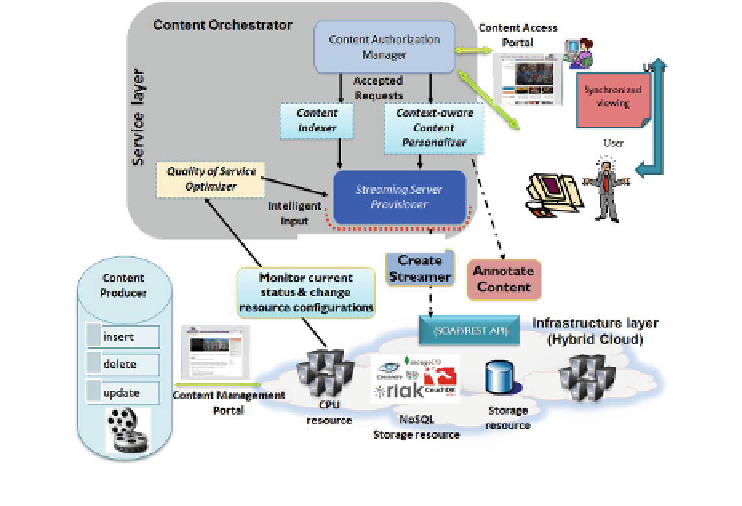
Fig. 8. The MediaWise Cloud architecture [
14
]
via the content access/management portal. This dynamic content can also be annotated
using keywords for ef
cient indexing, search and retrieval. As soon as the request the
content is generated from a user(s), it is forwarded it to the MediaWise Cloud content
orchestrator (MCCO) [
39
].
MCCO is the heart of MediaWise cloud. It monitors hybrid clouds and provide
mechanisms for QoS-aware cloud selection, scheduling and admission control. For
example, as soon as the use request comes from the end user (via the content access
portal) for content processing and delivery, the MCCO decides which virtual machine
(VM) to provision out of several VMs running on several public clouds. This decision
is based on the type of request and the QoS status of the VM on a particular public
cloud. Hence, the MediaWise cloud offers QoS-based content placement, delivery as
well as compute functionality that is critical in matching end-user SLAs.
5.6 Codeen
Codeen is an academic CDN test-bed developed at Princeton university (
http://codeen.
cs.princeton.edu/
)
. It is primarily used to support services delivered the Planet Lab
project, a global research networks that supports developments of new network services.
Codeen has many proxy nodes distributed at various planet lab node locations. The
proxy perform the role of POPs and request redirectors. A number of related projects
that use the Codeen CDN include web-based content distribution service, name lookup,
Search WWH ::

Custom Search