Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
and exponential smoothing, for instance, are fil-
ters. Many known transformations are subsumed
by weighting functions. We consider the window
functions Bartlett, Hanning, Hamming, Black-
man-Harris, linear and exponential functions
as particular instances of a function
f
w
(
i
) which
weights the position within the window.
We define special instances of mark-up by as-
signing characteristic value types to intervals in
one of the dimensions of the considered space.
Definition 9
An
interval
I
:
S
→
C is a mark-up
within one dimension.
The segment S
= (
d,s,e
)
is
given by the dimension d, the starting point s,
and
the end point e. The characteristic E
= (
t,
ρ)
indicates a type t and a density
ρ
.
Definition 7
Given a value series
(
x
i
)
i
∈
{1
,…,n
}
, a
filter yi
i
=
f
w
(
i
)
⋅
x
i
is a
weight
filter
. The weighting
function f
w
only depends on the position i.
Often clustering (e.g., k-means) is used in
order to detect suitable intervals (Hastie, Tibshi-
rani, & Friedman, 2001). A clustering scheme is
only usable in dimensions with a nonequidistant
value distribution. Additionally, clustering in one
or several dimensions is a batch process to be
applied to the complete series. An incremental
process is the signal to symbol process (Morik
& Wessel, 1999):
Other filters are the frequency passes, filter-
ing the extremes, the Bark-filter, and the ERB
filter, which are all often used when analyzing
music data.
mark-up of Intervals
In analogy to mark-up languages for documents,
which annotate segments within a text, also seg-
ments within a value series can be annotated.
Signal to symbol processing:
•
Given the series (
x
i
)
i
∈
{1
,…,n
}
with
n
values, a
decision function
f
e
and an interval dimen-
sion,
Definition 8
A
mark
-
up
M
:
S
→
C assigns an
arbitrary characteristic C to
a segment S.
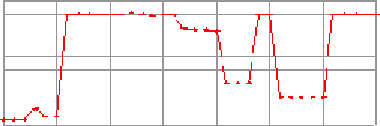
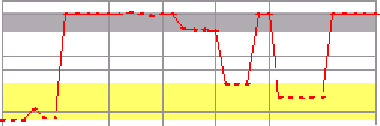
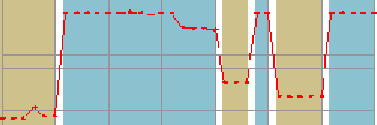
Figure 6. The process of finding intervals in a series (a), first in the value dimension (b), then projected
on the index dimension (c), delivering (d).
(a) Series
(b) Value Intervals
(c) Index Intervals
(d) Result

Search WWH ::

Custom Search