Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 2. Comparison of melodic fragments using the functional model
[m,n], it is possible to define different metrics; for
example the maximal (sup) difference between
the two functions or the “area” between the two
functions viewed as curves:
This is a very interesting metric because it
allows it to ignore differences between melodic
sequences given by transpositions.
In fact, starting from
i=1
implicates the exclu-
sion of the elements of
f
and
g
, so for example,
transposition of melodic sequences have zero
distance.
and
reductionistic approach
A typical mismatch of the functional approach
leads to be too much “note sensitive” in the sense
that themes with the same musical content may
appear very different from a functional point of
view.
As an example, in the following couple of
themes, the second is a very simple variation of
the first obtained by the introduction of a repeated
“a” between couples of notes.
Generalizing the concept, it is possible to make
an average of the higher order derivatives, like in
the Sobolev metric:
where
i
is the order of derivative.
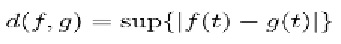
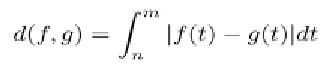








Search WWH ::

Custom Search