Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
2
EK test#1 with nano-iron
EK test#2 with nano-iron
EK test w/o nano-iron
Diffusion test with nano-iron
Oxidizing and acidic
1
Oxidizing and alkaline
Stable H
2
O
0
Passivity
Corrosion
-1
Immunity
Reducing and alkaline
-2
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
pH
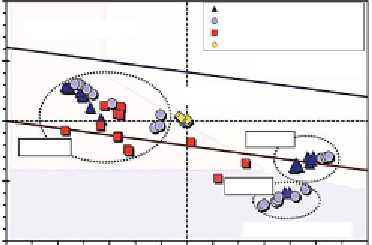
Figure 2.37
pH-ORP (Eh) variation of clay with and w/o nano-iron in electrokinetic
transport (Pamukcu et al., 2008)
low electrical fields, causing accumulation and higher charge density; but
pick up at regions of higher electric field, hence dilution and low charge
density. This process is likely to have a progressive nature that would allow
for self-correction by diffusion and Faradic currents to maintain the elec-
trical neutrality. Such a process could also result in the wave shape of the
voltage distribution to remain stationary with only the magnitudes of the
peaks changing. For example, if initially an accumulation were triggered
by a physical obstruction (i.e. agglomeration of the particles in small clay
pore-throats), voltage gradient at that locale would increase because of the
reduced conduction. The increased charge density would lead to surface
capacitance and Faradaic reactions at the location. At the same time, the
increased voltage gradient would promote the particles to move and vacate
the location, subsequently causing a drop in charge density, and reversal
of the surface reactions. It is difficult to capture such potential dynamics
through sporadic voltage and ORP measurements in a typical electroki-
netic transport testing in clay. Nevertheless, based on the data collected
and evaluated, the empirical evidence appears to support that presence of
clay and ensuing surface interactions enhance the ORP under direct cur-
rent electrical field.
The oscillating voltage gradients at high electrolyte concentration envi-
ronments were observed again in a large-scale test designed to mimic poten-
tial application of electrically assisted dewatering of sea-harbor sediments
(Muraoka et al., 2011). The model experiment simulated parallel vertical
electrodes that can be installed throughout the depth of unconsolidated
sediments allowing accelerated drainage laterally. Commercial kaolinite















Search WWH ::

Custom Search