Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
wastewater (Franz, 2002; Pulgarin et al., 1994). There has also been recent
evidence for the double layer-enhanced removal of Pb(II) (Ahn et al., 2010).
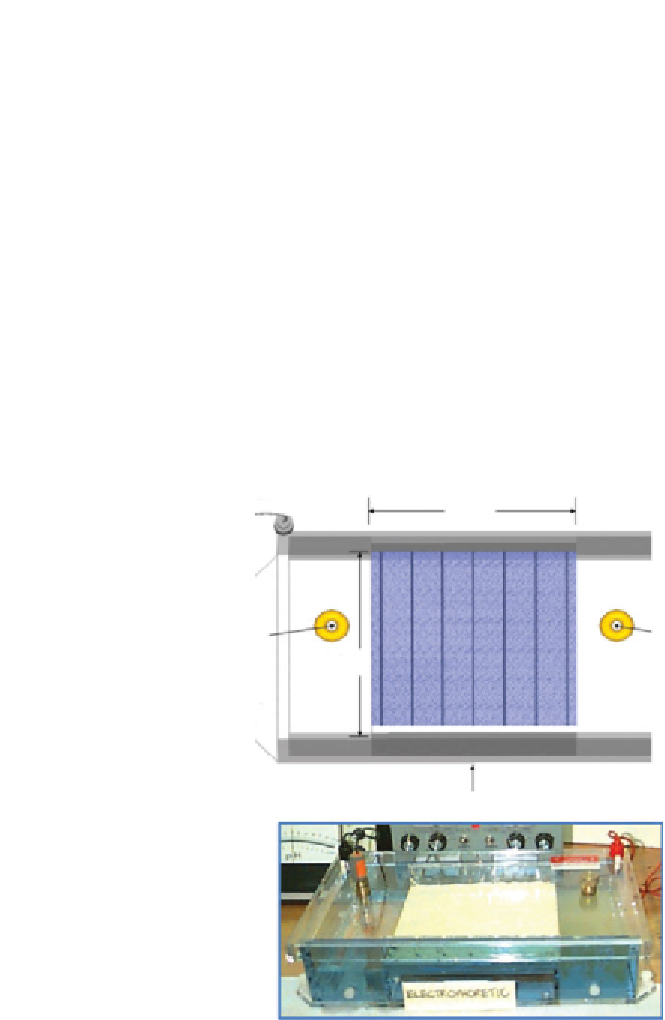
Previously, controlled laboratory experiments of kaolinite clay (see test set-
up in Figure 2.11) injected with Fe(II) showed that an externally applied
electric field caused an additional “cathodic current” that drive forth the
reduction of Cr(VI) in clay (Pamukcu et al., 2004). These transformations
were characterized as to have resulted from the capacitive changes on the
clay surfaces. The results in these experiments showed that the system ORP
(oxidation-reduction potential) increased by a positive shift from the stan-
dard solution ORP in the presence of the clay medium and the induced
electrical field. The ORP measurements were plotted against the reaction
quotient of the Nernst relation, where the data was categorized by pH, as
shown in Figure 2.12. The low pH range (pH range 2=>3) data showed the
best agreement with the linear fit, and the relative scatter of data at higher
pH values was attributed to poor polarization of the electric layer. At low
Cathode
20 cm
Calomel
Reference
Electrode
Port
(cathode)
18.5 cm
E7
E6
E5
E4
E3
E2
E1
Platinum electrodes
Figure 2.11
The electrophoretic set-up to measure enhanced transformation of Cr(IV) to
Cr(III) (Pamukcu et al., 2004, 2008; Hannum and Pamukcu, 2007)














Search WWH ::

Custom Search